Brother International 2011 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2011 Brother International annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
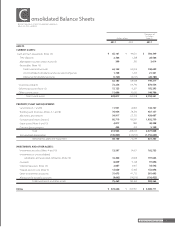
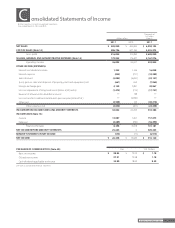
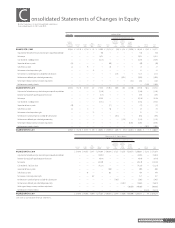
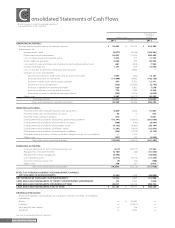
Brother Industries, Ltd. and Consolidated Subsidiaries
For the Years ended March 31, 2011 and 2010
26 Brother Annual Report 2011
(6) Cash Equivalents
Cash equivalents are short-term investments that are readily convertible into cash and that are exposed to insignificant risk of changes in value.
Cash equivalents include time deposits and investment trust, all of which mature or become due within three months of the date of
acquisition.
(7) Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. Cost is determined by the average method by the Company and consolidated manufactur-
ing subsidiaries. The consolidated sales subsidiaries determine cost by using the average method or the first-in, first-out method.
(8) Marketable and Investment Securities
Marketable and investment securities are classified and accounted for, depending on management’s intent, as follows:
i ) trading securities, which are held for the purpose of earning capital gains in the near term, are reported at fair value, and the related unrealized
gains and losses are included in earnings,
ii) held-to-maturity debt securities, which management has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity, are reported at amortized cost, and
iii) available-for-sale securities with market values, which are not classified as either of the aforementioned securities, are reported at fair value, with
unrealized gains and losses, net of applicable taxes, reported as a separate component of equity. Non-marketable available-for-sale securities
are stated at cost determined by the moving average method.
For other than temporary declines in fair value, marketable and investment securities are reduced to net realizable value by a charge to income.
(9) Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is mainly computed by the declining-balance method.
The range of useful lives was principally from 3 to 50 years for buildings and structures, from 4 to 12 years for machinery and vehicles and from
2 to 20 years for furniture and fixtures.
Depreciation of leased assets under finance leases is computed by the straight-line method over the lease period.
(10) Long-lived Assets
The Group reviews their long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstance indicate the carrying amount of an asset or
asset group may not be recoverable. An impairment loss would be recognized if the carrying amount of an asset or asset group exceeds the sum
of the undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from the continued use and eventual disposition of the asset or asset group. The impair-
ment loss would be measured as the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its recoverable amount, which is the higher of
the discounted cash flows from the continued use and eventual disposition of the asset or the net selling price at disposition.
(11) Other investments and assets
Intangible assets and goodwill are carried at cost less accumulated amortization, which is calculated by the straight-line method.
(12) Bonuses to directors and corporate auditors
Bonuses to directors and corporate auditors are accrued at the year end to which such bonuses are attributable.
(13) Warranty Reserve
The Group provided a warranty reserve for repair service to cover all repair expenses based on the past warranty experience.
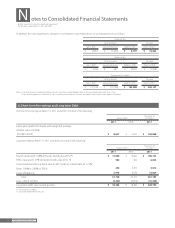
The warranty reserve was included in accrued expenses and amounted to ¥6,023 million ($72,566 thousand) and ¥7,215 million at March 31,
2011 and 2010, respectively.
(14) Liability for Retirement Benefits
(i) Employees’ Retirement Benefits
The Company has a contributory funded pension plan and a defined contribution pension plan covering substantially all of its employees.
Certain consolidated subsidiaries have non-contributory funded pension plans or unfunded retirement benefit plans. Also, certain foreign
subsidiaries have defined benefit pension plans and defined contribution pension plans.
As of October 1, 2009, the Company and certain consolidated subsidiaries switched part of their retirement benefit systems from a con-
tributory funded pension plan to a defined contribution pension plan. In accordance with this conversion, the Company and certain subsidiar-
ies have applied “Accounting for the Transfer between Retirement Benefit Plans” (ASBJ Guidance No.1, January 31, 2002). As a result of applying
this accounting standard, the Group recorded a ¥2,985 million loss on revision of benefit plan under other expenses for the year ended March
31, 2010.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements