Brother International 2009 Annual Report Download - page 27
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 27 of the 2009 Brother International annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
statements of income to the extent that they are not hedged by forward exchange contracts.
(20) Foreign Currency Financial Statements
The balance sheet accounts of the consolidated foreign subsidiaries are translated into Japanese yen at the current exchange rate as
of the balance sheet date except for equity, which is translated at the historical rate.
Differences arising from such translation are shown as “Foreign currency translation adjustments” in a separate component of the
equity and included in minority interests.
Revenue and expense accounts of consolidated foreign subsidiaries are translated into Japanese yen at the average exchange rate
during the year.
(21) Derivative and Hedging Activities
The Group uses derivative financial instruments to manage its exposures to fluctuations in foreign exchange and interest rates. For-
eign exchange forward contracts, interest rate swaps and currency option contracts are utilized by the Group to reduce foreign cur-
rency exchange and interest rate risks. The Group does not enter into derivatives for trading or speculative purposes.
Derivative financial instruments and foreign currency transactions are classified and accounted for as follows:
a) all derivatives are recognized as either assets or liabilities and measured at fair value, and gains or losses on derivative transactions
are recognized in the consolidated statements of income and
b) for derivatives used for hedging purposes, if derivatives qualify for hedge accounting because of high correlation and effectiveness
between the hedging instruments and the hedged items, gains or losses on derivatives are deferred until maturity of the hedged
transactions.
Foreign currency contracts and currency option contracts employed to hedge foreign exchange exposures are measured at fair
value and unrealized gains (losses) are recognized in income.
Foreign currency forward contracts and currency option contracts used to hedge forecasted (or committed) transactions are also
measured at fair value but the unrealized gains (losses) are deferred until the underlying hedged transactions are completed.
The interest rate swaps that qualify for hedge accounting and meet specific matching criteria are not remeasured at market value but
the differential paid or received under the swap agreements are recognized and included in interest expense or income.
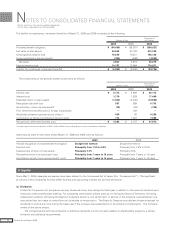
(22) Per Share Information
Basic net income per share is computed by dividing net income available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of
common shares outstanding for the period, retroactively adjusted for stock splits.
Diluted net income per share reflects the potential dilution that could occur if securities were exercised. Diluted net income per
share of common stock assumes full exercise of outstanding warrants at the beginning of the year (or at the time of issuance).
Cash dividends per share presented in the accompanying consolidated statements of income are dividends applicable to the
respective years including dividends to be paid after the end of the year.
(23) New Accounting Pronouncements
Business Combinations
On December 26, 2008, the ASBJ issued a revised accounting standard for business combinations, ASBJ Statement No.21, “Account-
ing Standard for Business Combinations.” Major accounting changes under the revised accounting standard are as follows:
(1) The current accounting standard for business combinations allows companies to apply the pooling of interests method of
accounting when certain specific criteria are met such that the business combination is essentially regarded as a uniting-of-
interests. The revised standard requires to account for such business combination by the purchase method and the pooling of
interests method of accounting is no longer allowed.
(2) The current accounting standard accounts for the research and development costs to be charged to income as incurred. Under
the revised standard, an in-process research and development (IPR&D) acquired by the business combination is capitalized as
an intangible asset.
(3) The current accounting standard accounts for a bargain purchase gain (negative goodwill) to be systematically amortized within
20 years. Under the revised standard, the acquirer recognizes a bargain purchase gain in profit or loss on the acquisition date
after reassessing whether it has correctly identified all of the assets acquired and all of the liabilities assumed with a review of
such procedures used.
This standard is applicable to business combinations undertaken on or after April 1, 2010 with early adoption permitted for fiscal years
beginning on or after April 1, 2009.
25Brother Annual Report 2009