AT&T Uverse 2007 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2007 AT&T Uverse annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
2007 AT&T Annual Report
| 57
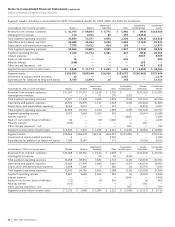
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Dollars in millions except per share amounts
NOTE 1. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation Throughout this document, AT&T Inc.
is referred to as “AT&T,” “we” or the “Company.” The
consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the
Company and our majority-owned subsidiaries and affiliates.
Our subsidiaries and affiliates operate in the communications
services industry throughout the U.S. and internationally,
providing wireless and wireline telecommunications services
and equipment as well as directory advertising and publishing
services. On December 29, 2006, we acquired 100% of
the outstanding common shares of BellSouth Corporation
(BellSouth). BellSouth is a wholly-owned subsidiary, and
the results of BellSouth’s operations have been included
in our consolidated financial statements after the
December 29, 2006 acquisition date. For a detailed
discussion of our acquisition, see Note 2.
All significant intercompany transactions are eliminated in
the consolidation process. Investments in partnerships, joint
ventures, and less-than-majority-owned subsidiaries where
we have significant influence are accounted for under the
equity method. Prior to the closing of the BellSouth
acquisition on December 29, 2006, we accounted for our
joint ventures with BellSouth under the equity method since
we shared control equally. Thus, for 2006 we recorded as
equity income our proportionate share of economic owner-
ship in these joint ventures, namely, 60% of AT&T Mobility LLC
(AT&T Mobility), formerly Cingular Wireless LLC, and 66% of
YELLOWPAGES.COM (YPC). AT&T Mobility and YPC became
wholly-owned subsidiaries of AT&T on December 29, 2006.
Earnings from certain foreign equity investments accounted
for using the equity method are included for periods ended
within up to one month of our year end (see Note 7).
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with
U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) requires
management to make estimates and assumptions that affect
the amounts reported in the financial statements and
accompanying notes, including estimates of probable losses
and expenses. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
FAS 159 In February 2007, the Financial Accounting
Standards Board (FASB) issued Statement of Financial
Accounting Standards No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for
Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities” (FAS 159). FAS 159
permits companies to choose to measure many financial
instruments and certain other items at fair value, providing the
opportunity to mitigate volatility in reported earnings caused
by measuring related assets and liabilities differently without
having to apply complex hedge accounting provisions. FAS 159
is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007.
We elected not to adopt the fair value option for valuation of
those assets and liabilities which are eligible, therefore there is
no impact on our financial position and results of operations.
FAS 160 In December 2007, the FASB issued Statement
of Financial Accounting Standards No. 160, “Noncontrolling
Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements – an amendment
of ARB No. 51” (FAS 160). FAS 160 requires noncontrolling
interests held by parties other than the parent in subsidiaries
be clearly identified, labeled, and presented in the
consolidated statement of financial position within equity,
but separate from the parent’s equity. FAS 160 is effective
for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008.
We are currently evaluating the impact FAS 160 will have
on our financial position and results of operations.
FAS 141(R) In December 2007, the FASB issued State-
ment of Financial Accounting Standards No. 141 (revised
2007), “Business Combinations” (FAS 141(R)). FAS 141(R) is a
revision of FAS 141 and requires that costs incurred to effect
the acquisition (i.e., acquisition-related costs) be recognized
separately from the acquisition. In addition, in accordance
with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 141,
“Business Combinations” (FAS 141), restructuring costs that
the acquirer expected but was not obligated to incur, which
included changes to benefit plans, were recognized as if they
were a liability assumed at the acquisition date. FAS 141(R)
requires the acquirer to recognize those costs separately from
the business combination. We are currently evaluating the
impact that FAS 141(R) will have on our accounting for
acquisitions prior to the effective date of the first fiscal year
beginning after December 15, 2008.
FIN 48 We adopted FASB Interpretation No. 48, “Accounting
for Uncertainty in Income Taxes” (FIN 48) on January 1, 2007.
FIN 48 clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in income taxes
recognized in an enterprise’s financial statements in accordance
with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 109,
“Accounting for Income Taxes.” The interpretation prescribes
a threshold for the financial statement recognition and
measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be
taken within an income tax return. For each tax position, the
enterprise must determine whether it is more likely than not
that the position will be sustained upon examination based on
the technical merits of the position, including resolution of
any related appeals or litigation. A tax position that meets the
more likely than not recognition threshold is then measured
to determine the amount of benefit to recognize within the
financial statements. No benefits may be recognized for tax
positions that do not meet the more likely than not threshold.
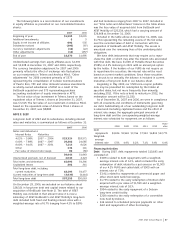
As required by FIN 48, on January 1, 2007, we reclassified
deferred income tax liabilities of $6,225 from our “Deferred
income taxes” for unrecognized tax benefits, of which $6,100
was included in “Other noncurrent liabilities” and $175 was
included in “Accrued taxes” on our consolidated balance
sheets and the remaining $50 was recorded as a reduction
to the beginning-of-year retained earnings to reflect the
cumulative effect of adoption of FIN 48 in the first quarter.
In May 2007, the FASB issued further guidance on whether
a tax position is effectively settled, the adoption of which
did not have a material impact on our financial position.
EITF 06-11 In June 2007, the Emerging Issues Task Force
(EITF) ratified the consensus on EITF 06-11, “Accounting for
Income Tax Benefits of Dividends on Share-Based Payment
Awards.” EITF 06-11 provides that a realized income tax
benefit from dividends or dividend equivalents that are
charged to retained earnings and are paid to employees for
nonvested equity-classified share-based awards and equity-
classified outstanding share options should be recognized
as an increase to additional paid-in capital rather than a
reduction of income tax expense. EITF 06-11 applies
prospectively to the income tax benefits that result from
dividends on equity-classified employee share-based payment
awards that are declared in fiscal periods beginning after
December 15, 2007. EITF 06-11 will not have a material
impact on our financial position and results of operations.
Reclassifications We have reclassified certain amounts
in prior-period financial statements to conform to the current
period’s presentation. Included among these, as a result of