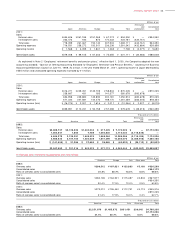
JVC 2002 Annual Report Download - page 36
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 36 of the 2002 JVC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ANNUAL REPORT 2 0 0 23 4
securities that are not classified in any of the above categories
(hereafter, “available-for-sale securities”).
Trading securities are stated at fair market value. Gains and losses
realized on disposal and unrealized gains and losses from market value
fluctuations are recognized as gains or losses in the period of the change.
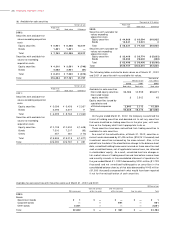
The Companies had no held-to-maturity debt securities. Equity
securities issued by subsidiaries and affiliated companies, which are
not consolidated or accounted for using the equity method, are stated
at moving-average cost. Available-for-sale securities with available fair
market values are stated at fair market value. Unrealized gains and
unrealized losses on these securities are reported, net of applicable
income taxes, as a separate component of stockholders’ equity.
Realized gains and losses on sale of such securities are computed
using moving-average cost. Other securities with no available fair
market value are stated at moving-average cost.
If the market value of equity securities issued by non-consolidated
subsidiaries and affiliated companies, and available-for-sale securities,
declines significantly, such securities are stated at fair market value
and the difference between fair market value and the carrying amount
is recognized as a loss in the period of the decline. If the fair market
value of equity securities issued by non-consolidated subsidiaries and
affiliated companies not accounted for by the equity method is not
readily available, such securities should be written down to net asset
value with a corresponding charge in the income statement in the
event net asset value declines significantly.
As a result of adopting the new accounting standard for financial
instruments, in the year ended March 31, 2001, income before
income taxes increased by ¥1,484 million. Also, based on the
examination of the intent of holding each security upon application
of the new accounting standard on April 1, 2000, trading securities
as well as available-for-sale securities maturing within one year from
the balance sheet date are included in current assets, and other
securities are included in investments and advances. As a result, at
April 1, 2000, securities in current assets decreased by ¥6,013
million and investment securities increased by the same amount
compared with what would have been reported under the previous
accounting policy.
Derivatives and hedge accounting
The new accounting standard for financial instruments, effective from
the year ended March 31, 2001, requires companies to state derivative
financial instruments at fair value and to recognize changes in the fair
value as gains or losses unless derivative financial instruments are used
for hedging purposes.
If derivative financial instruments are used as hedges and meet
certain hedging criteria, the Companies defer recognition of gains or losses
resulting from changes in fair value of derivative financial instruments
until the related losses or gains on the hedged items are recognized.
However, in cases where forward foreign exchange contracts are used
as hedges and meet certain hedging criteria, forward foreign exchange
contracts and hedged items are accounted for in the following manner:
1. If a forward foreign exchange contract is executed to hedge an
existing foreign currency receivable or payable,
(a) the difference, if any, between the Japanese yen amount of the
hedged foreign currency receivable or payable translated using the
spot rate at the inception date of the contract and the book value of
the receivable or payable is recognized in the income statement in the
period which includes the inception date, and
(b) the discount or premium on the contract (that is, the difference
between the Japanese yen amount of the contract translated using the
contracted forward rate and that translated using the spot rate at the
inception date of the contract) is recognized in the period which
includes the inception date.
2. If a forward foreign exchange contract is executed to hedge a future
transaction denominated in a foreign currency, the future transaction
will be recorded using the contracted forward rate, and no gains or
losses on the forward foreign exchange contract are recognized.
Also, if interest rate swap contracts are used as hedges and meet
certain hedging criteria, the net amount to be paid or received under
the interest rate swap contract is added to or deducted from the
interest on the assets or liabilities for which the swap contract
was executed.
Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment is stated at cost. Depreciation is
computed primarily by the declining-balance method at rates based
on the estimated useful lives of the assets. Certain consolidated
overseas subsidiaries use the straight-line method.
The ranges of useful lives for computing depreciation are generally
as follows:
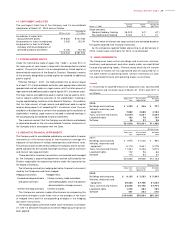
Buildings 20 to 50 years
Machinery and equipment 03to 07 years
Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to income
as incurred.
Software costs
In accordance with the provisional rule of the JICPA’s Accounting
Committee Report No.12 “Practical Guidance for Accounting for
Research and Development Costs, etc.” (the “Report”), the Company
accounts for software which was included in long-term prepaid
expenses in investments and other in the same manner in 2000 as in
1999. Pursuant to the Report, however, the Company included
software in other assets in 2002 and 2001. Software costs are
amortized using the straight-line method over the estimated useful
lives (three to five years).
Finance leases
Finance leases, except those leases for which the ownership of the leased
assets is considered to be transferred to the lessee, are accounted for in
the same manner as operating leases.
Research and development
Research and development expenditures for new products or improve-
ment of existing products are charged to income as incurred.
Income taxes
The Companies provided income taxes at the amounts currently pay-
able for the year ended March 31, 1999. Effective April 1, 1999,
the Companies adopted a New Accounting Standard, which recog-
nizes tax effects of temporary differences between the financial
statement basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities. Under
the new accounting standard, the provision for income taxes is com-
puted based on the pretax income included in the consolidated
statement of operations. The asset and liability approach is used to
recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future
tax consequences of temporary differences.
The amount of deferred income taxes attributable to the net tax
effects of the temporary differences at April 1, 1999, is reflected
as a cumulative adjustment of ¥27,259 million to the retained
earnings brought forward from the previous year. Prior years’ financial
statements have not been restated.