JVC 2002 Annual Report Download - page 35
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 35 of the 2002 JVC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
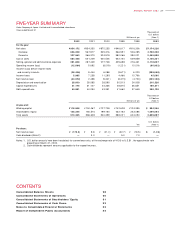
ANNUAL REPORT 2 0 0 2
3 3
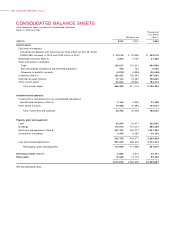
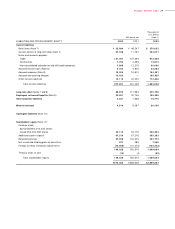
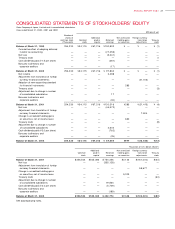
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEM ENTS
Victor Company of Japan, Limited and its consolidated subsidiaries
Years ended March 3 1, 2002, 2001 and 20 00
1 . BASIS OF PRESENTING CONSOLIDATED FINANCI AL
STATEMENTS
Victor Company of Japan (the “Company”) and its consolidated domestic
subsidiaries maintain their official accounting records in Japanese yen and
in accordance with the provisions set forth in the Japanese Commercial
Code and accounting principles and practices generally accepted in
Japan (“Japanese GAAP”). The accounts of overseas subsidiaries are
based on their accounting records maintained in conformity with
generally accepted accounting principles and practices prevailing
in the respective countries of domicile. Certain accounting principles
and practices generally accepted in Japan are different from International
Accounting Standards and standards in other countries in certain
respects as to application and disclosure requirements. Accordingly,
the accompanying consolidated financial statements are intended
for use by those who are informed about Japanese accounting principles
and practices.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been
restructured and translated into English (with some expanded descriptions
and the inclusion of consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity) from
the consolidated financial statements of the Company prepared in
accordance with Japanese GAAP and filed with the appropriate Local
Finance Bureau of the Ministry of Finance as required by the Securities
and Exchange Law. Some supplementary information included in the
statutory Japanese-language consolidated financial statements, but not
required for fair presentation is not presented in the accompanying
consolidated financial statements.
The translation of the Japanese yen amounts into U.S. dollars are
included solely for the convenience of readers, using the prevailing
exchange rate at March 31, 2002, which was ¥133 to U.S.$1.00.
The convenience translations should not be construed as representations
that the Japanese yen amounts have been, could have been, or could
in the future be, converted into U.S. dollars at this or any other rate
of exchange.
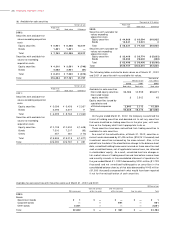
2 . SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the
Company and its significant subsidiaries. All significant intercompany
transactions and accounts have been eliminated.
Effective for the year ended March 31, 2000, all companies are
required to consolidate all significant investees, which are controlled
through substantial ownership of majority voting rights or existence of
certain conditions. Previously, only majority-owned companies were
consolidated. The prior years’ consolidated financial statements have
not been restated.
The effect of applying this rule to the Company’s consolidated
financial statements was immaterial.
Investments in certain unconsolidated subsidiaries and affiliated
companies (20% to 50% owned and certain others 15% to 20% owned)
are, with minor exceptions, stated at their underlying net equity value
after elimination of unrealized intercompany profits and losses. The
Company’s investments in its remaining subsidiaries and affiliated com-
panies are immaterial in the aggregate, and are stated at cost or less.
The differences between acquisition cost and underlying net equity
at the time of acquisition are generally being amortized on the straight-
line method over five years.
Foreign currency translation
Current assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are
translated into Japanese yen at exchange rates prevailing at the balance
sheet dates except for those hedged by foreign currency forward
contracts, which are recorded at contract rates. Prior to April 1, 2000,
non-current assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies
were translated at historical exchange rates.
Effective April 1, 2000, the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries
(the “Companies”) adopted the revised accounting standard for foreign
currency translation (the “Revised Accounting Standard”). Under the
Revised Accounting Standard, long-term receivables and payables
denominated in foreign currencies are also translated into Japanese
yen at the year-end rate.
The effect on the consolidated statement of operations of adopting
the Revised Accounting Standard was immaterial.
Balance sheets of consolidated overseas subsidiaries are translated
into Japanese yen at the year-end rate except for stockholders’ equity
accounts, which are translated at the historical rates.
Statements of operations of consolidated overseas subsidiaries are
translated at average rates except for transactions with the Company,
which are translated at the rates used by the Company.
Due to the adoption of the Revised Accounting Standard, the Company
reports foreign currency translation adjustments in stockholders’ equity
and minority interests. The prior year’s amount, which is included in
assets, has not been reclassified.
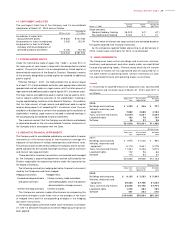
Cash and cash equivalents
In preparing the consolidated statement of cash flows for the years
ended March 31, 2002, 2001 and 2000, cash on hand, readily
available deposits and short-term highly liquid investments with
maturities not exceeding three months at the time of purchase are
considered to be cash and cash equivalents.
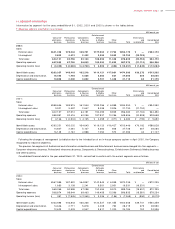
Inventories
Inventories are stated at cost, which is determined primarily by the
average-cost method.
Securities
Prior to April 1, 2000, publicly-traded securities were stated at the
lower of cost or market, and the other securities were stated at cost.
Cost was determined using the moving-average method. Securities of
consolidated subsidiaries in the United States were accounted for in
accordance with the Statement of Financial Accounting Standards
No.115 by the Financial Accounting Standards Board.
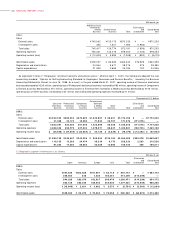
Effective April 1, 2000, the Companies adopted the new Japanese
accounting standard for financial instruments (“Opinion Concerning
Establishment of Accounting Standard for Financial Instruments”
issued by the Business Accounting Deliberation Council on January
22, 1999).
Upon applying the new accounting standard, all companies are
required to examine the intent of holding each security and classify
those securities as (a) securities held for trading purposes (hereafter,
“trading securities”), (b) debt securities intended to be held to maturity
(hereafter, “held-to-maturity debt securities”), (c) equity securities
issued by subsidiaries and affiliated companies, or (d) for all other