Home Depot 1999 Annual Report Download - page 31
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 31 of the 1999 Home Depot annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
The Home Depot, Inc. and Subsidiaries
The amount of goodwill impairment, if any, is measured based on
projected discounted future operating cash flows using a discount
rate reflecting the Company’s average cost of funds.
Store Pre-Opening Costs
Non-capital expenditures associated with opening new stores are
expensed as incurred.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company reviews long-lived assets for impairment when
circumstances indicate the carrying amount of an asset may not be
recoverable. An impairment is recognized to the extent the sum of
undiscounted estimated future cash flows expected to result from the
use of the asset is less than the carrying value. Accordingly, when the
Company commits to relocate or close a store, the estimated unre-
coverable costs are charged to selling and store operating expense.
Such costs include the estimated loss on the sale of land and build-
ings, the book value of abandoned fixtures, equipment and leasehold
improvements, and a provision for the present value of future lease
obligations, less estimated sub-lease income.
Stock Compensation
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 123 (“SFAS 123”),
“Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation,” encourages the use
of a fair-value-based method of accounting. As allowed by SFAS 123,
the Company has elected to account for its stock-based compensation
plans under the intrinsic value-based method of accounting prescribed
by Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 25 (“APB No. 25”),
“Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees.” Under APB No. 25,
compensation expense would be recorded on the date of grant if the
current market price of the underlying stock exceeded the exercise price.
The Company has adopted the disclosure requirements of SFAS 123.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income includes net earnings adjusted for certain
revenues, expenses, gains and losses that are excluded from net earn-
ings under generally accepted accounting principles. Examples include
foreign currency translation adjustments and unrealized gains and
losses on investments.
Foreign Currency Translation
The assets and liabilities denominated in a foreign currency are trans-
lated into U.S. dollars at the current rate of exchange on the last day
of the reporting period, revenues and expenses are translated at the
average monthly exchange rates, and all other equity transactions are
translated using the actual rate on the day of the transaction.
Use of Estimates
Management of the Company has made a number of estimates and
assumptions relating to the reporting of assets and liabilities and the
disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities to prepare these financial
statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting princi-
ples. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
Reclassifications
Certain balances in prior fiscal years have been reclassified to conform
with the presentation in the current fiscal year.
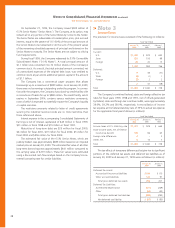
>Note 2
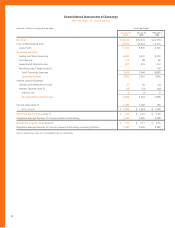
Long-Term Debt
The Company’s long-term debt at the end of fiscal 1999 and 1998
consisted of the following (amounts in millions):
January 30, January 31,
2000 1999
31⁄4% Convertible Subordinated Notes,
due October 1, 2001; converted into
shares of common stock of the Company
at a conversion price of $15.3611 per
share in October 1999 $–$ 1,103
61⁄2% Senior Notes, due September 15, 2004;
interest payable semi-annually on March 15
and September 15 beginning in 2000 500 –
Commercial Paper; weighted average
interest rate of 4.8% at January 31, 1999 –246
Capital Lease Obligations; payable in varying
installments through January 31, 2027
(see note 5) 216 180
Installment Notes Payable; interest imputed
at rates between 5.2% and 10.0%; payable
in varying installments through 2018 45 27
Unsecured Bank Loan; floating interest rate
averaging 6.05% in fiscal 1999 and 5.90%
in fiscal 1998; payable in August 2002 15 15
Variable Rate Industrial Revenue Bonds;
secured by letters of credit or land; interest
rates averaging 2.9% during fiscal 1999
and 3.8% during fiscal 1998; payable in
varying installments through 2010 39
Total long-term debt 779 1,580
Less current installments 29 14
Long-term debt, excluding current installments $ 750 $ 1,566
27