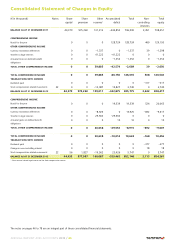
TomTom 2013 Annual Report Download - page 50
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 50 of the 2013 TomTom annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Performance share plan
Cash-settled share-based payments are initially recognised at the fair value of the liability and are expensed over the vesting period. The liability
is remeasured at each balance sheet date to its fair value, with all changes recognised immediately as either a profit or a loss.
Taxation
Income tax expense represents the sum of the tax currently payable and deferred tax. The group's income tax expense is calculated using tax
rates that have been enacted or substantively enacted at the balance sheet date.
Deferred taxes are calculated using the liability method. Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between
the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. Deferred tax
assets and liabilities are measured using the tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences
are expected to be recovered or settled, using tax rates (and laws) that have been enacted or substantially enacted by the balance sheet date.
The measurement of deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets reflects the tax consequences that would follow from the manner in which
the group expects, at the balance sheet date, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities.
Deferred tax assets are recognised when it is probable that sufficient taxable profits will be available against which the deferred tax assets
can be utilised. The carrying amounts of deferred tax assets are reviewed at each balance sheet date and reduced to the extent that it is no
longer probable that sufficient taxable profits will be available to allow all or part of the asset to be recovered.
Current and deferred taxes are recognised as an expense or income in the profit and loss account, except when they relate to items credited
or debited directly to equity. In this case, the tax is also recognised directly in equity, or where it arises from the initial accounting for a business
combination.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the cost of an acquisition over the fair value of the group's share of the net identifiable assets of the acquired
subsidiary/associate at the date of acquisition. Goodwill on acquisitions is tested at least annually for impairment and carried at cost less
accumulated impairment losses. Goodwill is allocated to operating segments for the purpose of impairment testing. The allocation is made
to those operating segments that are expected to benefit from the business combination in which the goodwill arose.
Intangible assets other than goodwill
Internally generated intangible assets
Internal software development costs relating to core technology are recognised as an intangible asset if, and only if, all of the following have
been demonstrated:
• The technical feasibility to complete the project;
• The intention to complete the intangible asset, and use or sell it;
• The ability to use or sell the intangible asset;
• How the intangible asset will generate probable future economic benefits;
• The availability of adequate resources to complete the project; and
• The cost of developing the asset can be measured reliably.
Internally generated databases are capitalised until a certain level of map coverage is reached and on-going activities focus on maintenance.
At this point capitalisation is discontinued.
The amount initially recognised for internally generated intangible assets is the sum of the expenditure incurred from the date when the
intangible asset first meets the recognition criteria listed above.
All expenditures on research activities are expensed in the income statement as incurred. Internal software costs relating to development of
non-core software with an estimated average useful life of less than one year and engineering costs relating to the detailed manufacturing
design of new products are expensed in the period in which they are incurred.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements / Continued
ANNUAL REPORT AND ACCOUNTS 2013 / 50