JVC 2006 Annual Report Download - page 54
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 54 of the 2006 JVC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
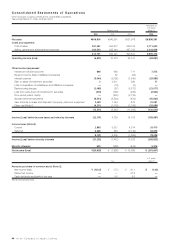
52 Victor Company of Japan, Limited
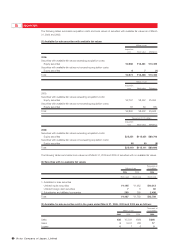
SHORT-TERM BANK LOANS AND LONG-TERM DEBT
Short-term bank loans of certain of the Company’s consolidated subsidiaries consist of notes maturing generally in
three months. The applicable annual interest rates on short-term bank loans outstanding at March 31, 2006 and
2005 range from 0.01% to 17.35% and from 0.01% to 12.81%, respectively.
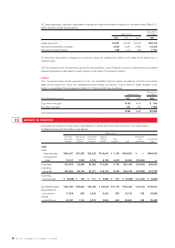
Long-term debt at March 31, 2006 and 2005 is as follows:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
2006 2005 2006
0.55% unsecured convertible bonds due in 2005 ¥—¥19,528 $—
2.15% unsecured bonds due in 2005 —9,500 —
1.68% unsecured bonds due in 2006 20,000 20,000 170,940
1.89% unsecured bonds due in 2007 10,000 10,000 85,470
1.50% guaranteed notes due in 2005 —7,073 —
Loans, primarily from banks with interest principally at 1.19% to 6.10%:
Unsecured 30,354 20,479 259,436
60,354 86,580 515,846
Less current portion 20,139 56,235 172,128
¥40,215 ¥30,345 $343,718
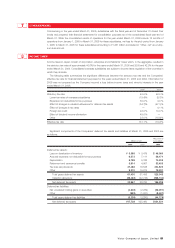
The aggregate annual maturities of long-term debt at March 31, 2006 are as follows:
Thousands of
Year ending March 31 Millions of yen U.S. dollars
2007 ¥20,139 $172,128
2008 10,142 86,684
2009 30,073 257,034
¥60,354 $515,846
EMPLOYEES’ SEVERANCE AND RETIREMENT BENEFITS
Employees of Japanese companies are compulsorily included in the Welfare Pension Insurance Scheme enacted
by the national government. Employers are legally required to deduct employees’ welfare pension insurance contri-
butions from their payroll and to pay them to the government together with employers’ own contributions. For
companies that have established their own Employees’ Pension Fund which meets certain legal requirements, it is
possible to transfer a part of their welfare pension insurance contributions (referred to as the substitutional portion
of the government’s scheme) to their own Employees’ Pension Fund under the government’s permission and
supervision.
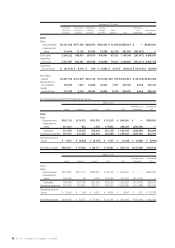
Liability for employees’ retirement benefits included in liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets for 2006 and
2005 and the related expenses for 2006, 2005 and 2004, which were determined based on the amounts obtained
by actuarial calculations, are as follows:
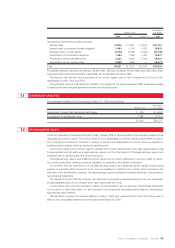
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
2006 2005 2006
Projected benefit obligation:
Projected benefit obligation ¥(129,213) ¥(133,997) $(1,104,385)
Unamortized prior service costs (15,985) (17,866) (136,624)
Unamortized actuarial differences 6,693 21,893 57,205
Less fair value of plan assets 111,471 97,470 952,744
Less unrecognized net transition obligation 14,428 16,016 123,316
Liability for severance and retirement benefits ¥0(12,606) ¥0(16,484) $0,(107,744)
10
9