JVC 2006 Annual Report Download - page 50
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 50 of the 2006 JVC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
48 Victor Company of Japan, Limited
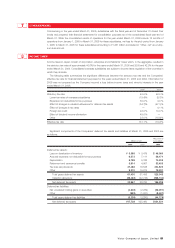
Securities
Securities are classified as (a) securities held for trading purposes (“trading securities”), (b) debt securities intended
to be held to maturity (“held-to-maturity debt securities”), (c) equity securities issued by subsidiaries and affiliated
companies, and (d) for all other securities that are not classified in any of the above categories (“available-for-sale
securities”).
The Company and its consolidated subsidiaries (“the Companies”) had no trading securities or held-to-maturity
debt securities. Equity securities issued by subsidiaries and affiliated companies which are not consolidated or
accounted for by the equity method, are stated at moving-average cost. Available-for-sale securities with available
fair market values are stated at fair market value. Unrealized gains and losses on these securities are reported, net
of applicable income taxes, as a separate component of stockholders’ equity. Realized gains and losses on sale of
such securities are computed using moving-average cost. Other securities with no available fair market value are
stated at moving-average cost.
If the market value of equity securities issued by non-consolidated subsidiaries and affiliated companies, and
available-for-sale securities, declines significantly, such securities are stated at fair market value and the difference
between fair market value and the carrying amount is recognized as a loss in the period of the decline. If the fair mar-
ket value of equity securities issued by non-consolidated subsidiaries and affiliated companies not accounted for by
the equity method is not readily available, such securities should be written down to net asset value with a corre-
sponding charge in the income statement in the event when net asset value declines significantly.
Derivatives and hedge accounting
The Companies state derivative financial instruments at fair value and recognize changes in the fair value as gains
or losses unless derivative financial instruments are used for hedging purposes.
If derivative financial instruments are used as hedges and meet certain hedging criteria, the Companies defer
recognition of gains or losses resulting from changes in fair value of derivative financial instruments until the related
losses or gains on the hedged items are recognized.
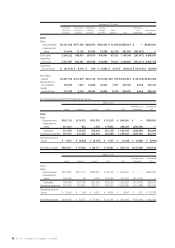
Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is computed primarily by the declining-balance
method based on the estimated useful lives of the assets. Certain consolidated overseas subsidiaries use the
straight-line method.
The ranges of useful lives for computing depreciation are generally as follows:
Buildings 20 to 50 years
Machinery and equipment 3 to 7 years
Finance leases
Finance leases, except those leases for which the ownership of the leased assets is considered to be transferred
to the lessee, are accounted for in the same manner as operating leases.
Research and development expenditures
Research and development expenditures for the development of new products or the significant improvement of
existing products are charged to income as incurred.
Income taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recog-
nized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carry-
ing amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and net operating loss carried forward
and foreign tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates
expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recov-
ered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in
the period that includes the enactment date.
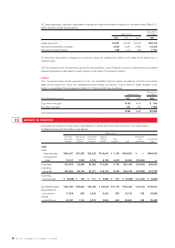
Employees’ severance and retirement benefits
The Company and some domestic subsidiaries have funded pension plans and unfunded benefit plans to provide
retirement benefits for substantially all employees.
Upon retirement or termination of employment for reasons other than dismissal for cause, eligible employees are
entitled to lump-sum and/or annuity payments based on the current rates of their salary and length of service.
The liabilities and expenses for severance and retirement benefits are determined based on the amounts actuari-
ally calculated using certain assumptions.