Columbia Sportswear 2001 Annual Report Download - page 35
Download and view the complete annual report
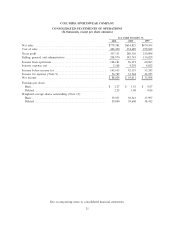
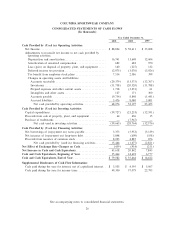
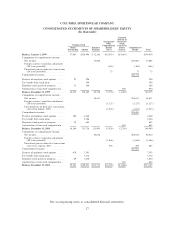
Please find page 35 of the 2001 Columbia Sportswear annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.COLUMBIA SPORTSWEAR COMPANY
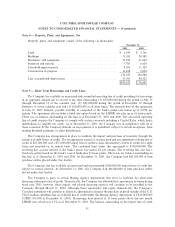
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Ì (Continued)
Property, plant, and equipment:
Property, plant, and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation of machinery and equipment, furniture
and Ñxtures and amortization of leasehold improvements is provided using the straight-line method over the
estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from 3 to 10 years. Buildings are depreciated using the straight-
line method over 30 years.
The interest-carrying costs of capital assets under construction are capitalized based on the Company's
weighted average borrowing rates. Capitalized interest was $792,000, $145,000 and $281,000 in 2001, 2000
and 1999, respectively.
Intangibles and other assets:
In September 2000, the Company acquired the Sorel trademark rights, associated brand names and other
related intellectual property rights for $7,967,000 in cash. The acquired intangible assets are being amortized
over their estimated useful lives on a straight-line basis over ten years. The related accumulated amortization
was $996,000 and $199,000 at December 31, 2001 and 2000, respectively.
Impairment of long-lived and intangible assets:
The Company evaluates the carrying value of long-lived assets for possible impairment as events or
changes arise indicating that such assets should be reviewed. If an asset is determined to be impaired, the loss
is measured as the amount by which the carrying value of the asset exceeds its fair value. Fair value is based
on the best information available, including prices for similar assets or the results of valuation techniques. The
Company has determined that its long-lived assets as of December 31, 2001 and 2000 are not impaired.
Deferred income taxes:
Deferred income taxes are provided for temporary diÅerences between the amount of assets and liabilities
for Ñnancial and tax reporting purposes. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when it is
estimated to be more likely than not that some portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Revenue Recognition:
Revenue for wholesale operations and licensing is recognized at the time the merchandise is shipped to
customers. Retail store revenue is recognized at the time of sale. Allowances for estimated returns are
provided when sales are recorded.
Foreign currency translation:
The assets and liabilities of the Company's foreign subsidiaries have been translated into U.S. dollars
using the exchange rates in eÅect at period end, and the net sales and expenses have been translated into U.S.
dollars using average exchange rates in eÅect during the period. The foreign currency translation adjustments
are included as a separate component of shareholders' equity and are not currently adjusted for income taxes
as they relate to indeÑnite net investments in non-U.S. operations.
Fair value of Ñnancial instruments:
Based on borrowing rates currently available to the Company for bank loans with similar terms and
maturities, the fair value of the Company's long-term debt approximates the carrying value. Furthermore, the
carrying value of all other Ñnancial instruments potentially subject to valuation risk (principally consisting of
cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable) also approximate fair value because of
their short-term maturities.
29