Redbox 2009 Annual Report Download - page 79
Download and view the complete annual report
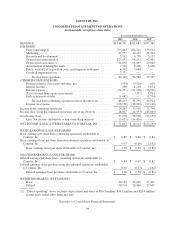
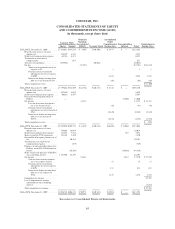
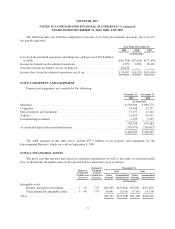
Please find page 79 of the 2009 Redbox annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.COINSTAR, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2009, 2008, AND 2007
not actively traded in the market. The transaction costs directly associated with the issuance were proportionally
allocated to the liability and equity components. In addition, we recorded deferred tax assets according to FASB
ASC 740-10-45, Deferred Tax Accounts Related to an Asset or Liability. The amortization of the debt discount is
based on the interest rate method and is to be recognized as non-cash interest expense.
Recognition and reporting of business dispositions: When management commits to a plan to dispose of a
business component, it is necessary to determine how the results will be presented within the financial statements
and whether the net assets of that business are recoverable. Our significant accounting policies and judgments
associated with a decision to dispose of a business are as follows:
•Assets held for sale- We define a business component as held for sale if it meets the criteria of assets
held for sale within FASB ASC 360-10-45 at the balance sheet date. Upon being classified as held for
sale, the recoverability of the carrying value of the business must be assessed, and the business held for
sale is reported at the lower of its carrying value or fair value less cost to sell.
•Discontinued operations- We define a business component that has either been disposed of or is classified
as held for sale as discontinued operations if its operations and cash flows are clearly distinguishable from
the rest of the entity; its operations and cash flows have been or will be eliminated from ongoing
operations of the entity as a result of the disposal; and we have no significant continuing involvement in
the operations of the component after the disposal transaction. If a component is recorded as discontinued
operations, the results of operations of the disposed business through the date of sale and the gain or loss
on disposal are presented on a separate line in the income statement for all periods presented.
See discussion of the sale of our Entertainment Business in Note 4 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Recent accounting pronouncements: In July 2009 the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting
Standards No. 168, The Accounting Standards Codification and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles (“SFAS 168”). SFAS 168 became the source of authoritative GAAP recognized by the FASB to be
applied by nongovernmental entities. Rules and interpretive releases of the SEC under authority of federal
securities laws are also sources of authoritative GAAP for SEC registrants. On the effective date of SFAS 168,
the Codification superseded all then-existing non-SEC accounting and reporting standards. All other
nongrandfathered non-SEC accounting literature not included in the Codification became nonauthoritative. This
Statement is effective for financial statements issued for interim and annual periods ending after September 15,
2009. The adoption of SFAS 168 did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial position, results of
operations, or cash flows. We have made references to the accounting standards codification throughout the
disclosures in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
In May 2009, the FASB issued FAS 165 which is now incorporated within FASB ASC 855. The new
guidance addresses accounting and disclosure requirements related to subsequent events. The objective of the
new guidance is to establish general standards of accounting for and disclosure of events that occur after the
balance sheet date but before the financial statements are issued or available to be issued. FASB ASC 855 sets
forth:
1. The period after the balance sheet date during which management of a reporting entity should evaluate
events or transactions that may occur for potential recognition or disclosure in the financial statements;
2. The circumstances under which an entity should recognize events or transactions occurring after the
balance sheet date in its financial statements; and
3. The disclosures that an entity should make about events or transactions that occurred after the balance
sheet date.
73