Nissan 2012 Annual Report Download - page 38
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 38 of the 2012 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Additionally, based on the policy of contribution to local society, we reacted rapidly to provide rest
space to people who could not return home on March 11 and to support damaged areas.
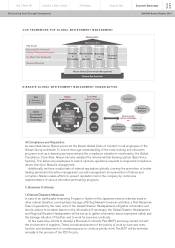
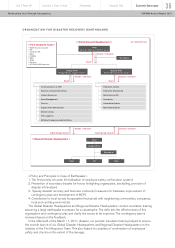
At the stage of business recovery, the Disaster Headquarters and the project teams of each
function continuously shared up-to-date information and were addressing the issues for production
and business recovery with companywide cooperation. It was effective for the quick recovery of our
total supply chain, including parts supply, production, logistics, sales and services.
The response to the March 2011 disaster was reviewed during fiscal 2011 to identify issues that
came to light on a function-by-function basis and to consider countermeasures. In March 2012,
simulation training was conducted based on a new scenario incorporating the review findings, and the
new measures were verified.
Utilizing the PDCA cycle, disaster measures will be advanced to address additional issues raised
during training and in response to recent changes in the government’s anticipated seismic scale
announcements. The Global Headquarters building, where the Disaster Headquarters has been set up
(built in August 2009), has an earthquake-resistant structure using vibration-controlling brace
dampers. Safety is assured even in the case of a maximum-level earthquake at the site. Inspections
after the earthquake confirmed that the building had no problems whatsoever with its safety and
functions.
2) Pandemic
In response to the outbreak of H1N1 type influenza in April 2009, Nissan established a global policy
for infection prevention. Each region has organized a response team and has promoted concrete
countermeasures based on the policy. Infection status can be monitored globally thanks to firmly
developed reporting lines between the global response team and each regional team.
Nissan has promoted countermeasures based on three basic principles stated in the global policy,
which are:
1. First priority on employees’ health and lives
2. Prevention of the spread of infection
3. Continuity of business operation
As specific actions, Nissan established the “guidelines for employees’ action” which stipulated
actions to be taken by employees, Sections and Companies, and kept employees informed.
Nissan also developed a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) for each business section, with several
triggers to invoke the BCP depending on the infection ratio, to maintain business continuity even
under a high infection situation.
Nissan will keep prepared for contingencies like avian flu through its PDCA cycle, such as by
updating response team members and the BCP, carrying out educational activities for infection
prevention and stockpiling sanitary and medical goods.
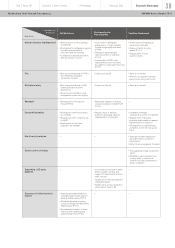
3) Countermeasures for Production Continuity Risk
Nissan’s production division has dealt with various risks related to the three elements of production, as
listed in the chart below. Particularly for natural disasters, we have worked over the years on
continuous prevention countermeasures to physical infrastructure (quakeproofing and reinforcement
of buildings and other facilities), maintained an operations recovery manual to shorten recovery time
and regularly executed BCP simulation drills. Learning from the lessons of the Great East Japan
Earthquake and the floods in Thailand, we are reviewing and strengthening our activities. More
specifically, we have set the period after which production is to be resumed following a large-scale
disaster to two weeks, and we have clarified necessary measures and produced action plans so that
this can be achieved. In each business facility, the operations recovery manual has been improved with
the addition of more practical content. We have begun regular audits of the manuals to confirm that
they are in the proper condition to be executed as written.
In addition to such countermeasures to natural disasters, it is absolutely important to manage risks
associated with parts procured from Leading Competitive Countries (LCCs) in order to expand
markets globally. To deal with such risk, Nissan has been conducting risk assessment before making
sourcing decisions, providing support for improvement activities after sourcing, implementing quality
checks at key points in the production and logistics process to prevent the production and utilization of
imperfect parts and enhancing activities to minimize supply capacity risk in order to secure global
market expansion and growth.
Innovation & Power of brandYear 2 Power 88 Performance Corporate Data
Corporate Governance 37
NISSAN Annual Report 2012Maintaining Trust Through Transparency