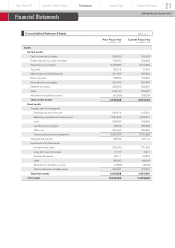
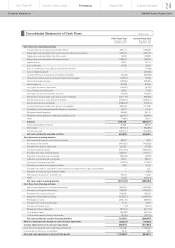
Nissan 2012 Annual Report Download - page 32
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 32 of the 2012 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
2) Financial Market
Nissan is exposed to various financial-market-related risks, such as foreign exchange, interest rate
and commodity price. It is Nissan’s general policy not to use derivative products as a primary tool to
manage foreign exchange and commodity price risks, as it will not provide a permanent solution to
mitigate the risks. In some cases, Nissan does hedge select currencies and commodity price risks.
Nissan is taking the following measures to minimize financial market risks.
Foreign exchange
As a company engaged in export activities, Nissan is faced with various foreign currency exposures
which results from the currency of input cost being different from the currency of sale to customer. In
order to minimize foreign exchange risk on a more permanent basis, Nissan is working to reduce
foreign currency exposure by such measures as shifting production to the countries where vehicles
are sold, and procurement of raw material and parts in foreign currencies. In the short term, Nissan
may hedge risks in foreign exchange volatility within a certain range by using derivative products in
accordance with the internal policies and procedures for risk management and operational rules
regarding derivative transactions.
Interest rate
The interest rate risk management policy is based on two principles: long-term investments and a
permanent portion of working capital are financed at fixed interest rates while the non-permanent
portion of working capital and liquidity reserves are built at floating rates.
Commodity price
Nissan purchases raw materials in the form of parts provided by suppliers, as well as direct purchases.
Nissan is exposed to the price fluctuation risks of raw materials, no matter whether it is purchased
directly or indirectly.
For precious metals, which are used as catalyst, Nissan is making continuous efforts to reduce their
usage through technological innovation, in order to minimize commodity price risks. In the short term,
Nissan manages commodity price volatility exposure through the use of fixed rate purchase contracts
where the commodity price is fixed for a period of time, and Nissan may also hedge risks in commodity
price volatility within a certain range by the use of derivative products in accordance with the internal
policies and procedures for risk management and operational rules regarding derivative transactions.
3) Sales Finance
Interest rate risk management
The sales financing business is exposed to interest rate risks. Interest rate risk is defined as the
potential variance in the earnings of an entity or the fair value of the portfolio that would result from a
fluctuation in the general level of market interest rates where funds with differing fixed-rate periods or
differing terms are financed and invested.
Nissan measures the risks by using sensitivity analysis with various interest rate scenarios and
determines the risk tolerance level. Nissan controls the interest rate maturities of both assets and
liabilities to maintain the risks within the acceptable tolerance level.
The sensitivity analysis mentioned above uses statistical models, such as the Monte Carlo
simulation method. However, actual fluctuations of market interest rates and their impact may deviate
significantly from the assumptions used in the model.
Nissan enters into interest rate derivative financial instruments to maintain the potential variability of
interest rates at a desired level of risk exposure. The main objective of these transactions is to mitigate
the risks and not to pursue speculative profit maximization.
Credit risks
Nissan is exposed to the risks of failure to recover the full value of financial receivables in its auto
credit and lease business with retail customers and its dealer finance business, due to changes in the
economic situation and the credit quality of customers. Nissan manages the credit risks closely by
establishing effective screening and collection systems and structures.
Credit applicants are all subject to credit assessments of their creditworthiness under a detailed
scoring system. Based on the information directly obtained from applicants and from credit bureaus,
Innovation & Power of brandYear 2 Power 88 Performance Corporate Data
Corporate Governance 31
NISSAN Annual Report 2012Maintaining Trust Through Transparency