Nissan 2012 Annual Report Download - page 36
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 36 of the 2012 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
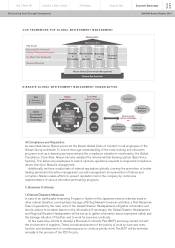
OUR FRAMEWORK FOR GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT MANAGEMENT
Sincere Eco-Innovator
Nissan Global Environment Management
Communication
Stakeholders
Marketing
&
Sales
Manufacturing
&
Logistics
Business
Partners
Products
&
Technology
Marketing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing
Products
Reducing CO2 Emissions/
Shifting to Renewable Energies
Key Issues
Resource Recycling
Marketing
&
Sales
Manufacturing
Manufacturing
&
Logistics
Business
Partners
Products
&
Technology
Technology
Air, Water, Soil, Biodiversity
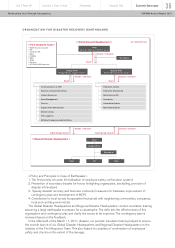
CEO
Executive
Committee
Global
Environment
Management
Committee
Global,
corporate focuses
PDCA
PDCA
PDCA
Plan
Check
DoAct
Global
Environmental
Planning
Office
Functional,
regional focuses Customers
Shareholders
and investors
Communities
and future
generations
Employees Business
partners
Environmental
Advisory Meetings,
etc.
NISSAN’S GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT MANAGEMENT ORGANIZATION
4) Compliance and Reputation
As described above, Nissan produced the Nissan Global Code of Conduct for all employees of the
Nissan Group worldwide. To ensure thorough understanding of the code, training and education
programs such as e-learning are improved and the compliance situation is monitored by the Global
Compliance Committee. Nissan has also adopted the internal whistle blowing system (Easy Voice
System). This allows any employees to submit opinions, questions, requests or suspected compliance
issues directly to Nissan’s management.
Additionally, we have created sets of internal regulations globally covering the prevention of insider
trading, personal information management, records management and prevention of bribery and
corruption. Nissan makes efforts to prevent reputation risk to the company by continuous
implementation of various education and training programs.
3. Business Continuity
1) Natural Disasters Measures
In case of an earthquake measuring 5-upper or higher on the Japanese seismic intensity scale or
other natural disasters causing heavy damage affecting Nissan’s business activities, a First Response
Team (organized by the main units of the Global Disaster Headquarters) will gather information and
decide actions to be taken based on the information. If necessary, the Global Disaster Headquarters
and Regional Disaster Headquarters will be set up to gather information about employees’ safety and
the damage situation of facilities and to work for business continuity.
At the same time, efforts to develop a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) are being carried out with
the involvement of suppliers. These include assessment of the priority of work by each and every
function and development of countermeasures to continue priority work. The BCP will be reviewed
annually in the process of the PDCA cycle.
Innovation & Power of brandYear 2 Power 88 Performance Corporate Data
Corporate Governance 35
NISSAN Annual Report 2012Maintaining Trust Through Transparency