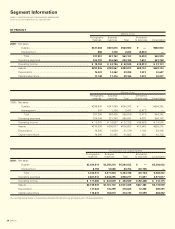
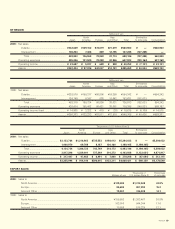
Konica Minolta 2000 Annual Report Download - page 26
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 26 of the 2000 Konica Minolta annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
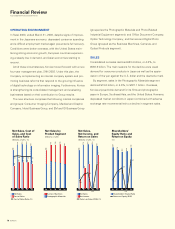
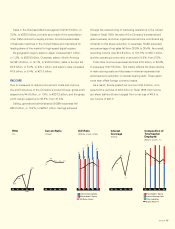
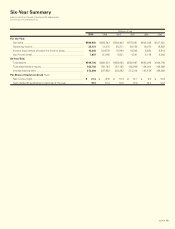
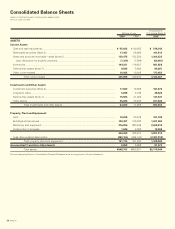
24 KONICA
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
KONICA CORPORATION AND CONSOLIDATED SUBSIDIARIES
1. Significant Accounting and Reporting Policies
(a) Basis of Presenting Financial Statements
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been
prepared based on the accounts maintained by Konica Corporation
(the “Company”) and its consolidated subsidiaries in accordance with
the provisions set forth in the Japanese Commercial Code (the “Code”)
and the Securities and Exchange Law and in conformity with account-
ing principles and practices generally accepted in Japan, which are
different in certain respects as to application and disclosure require-
ments of International Accounting Standards.
Certain items presented in the consolidated financial statements
submitted to the Director of Kanto Finance Bureau in Japan have
been reclassified in these accounts for the convenience of readers
outside Japan. In addition, the consolidated financial statements of
cash flows are not required to be filed with the Ministry of Finance
(MOF), but have been prepared and included in the consolidated
financial statements.
The consolidated statements of cash flows have been required to
be prepared with effect for the year ended March 31, 2000 in accor-
dance with new accounting standards. These new standards specify
a format which differs from that used in earlier years, and, according-
ly, the comparative periods’ consolidated statements of cash flows
have been reformatted.
(b) Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the
Company and, with certain exceptions which are not material, those
of its subsidiaries in which it has control. All significant intercompany
transactions and accounts and unrealized intercompany profits are
eliminated in consolidation.
Investments in unconsolidated subsidiaries and significant affiliates
are accounted for by the equity method. Investments in insignificant
affiliates are stated at cost.
The excess of cost over the underlying investments in subsidiaries
is recognized as goodwill and is amortized on a straight-line basis over
a five-year period.
(c) Translation of Foreign Currencies
Translation of Foreign Currency Transactions
Revenue and cost or expense items arising from the transactions
of the Company denominated in foreign currencies are translated
into Japanese yen at relevant exchange rates prevailing at the time
of transactions (“historical rates”).
All assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies (short-
term monetary items) are translated into yen at the historical rates.
Translation of Foreign Currency Financial Statements
The translations of foreign currency financial statements of overseas
consolidated subsidiaries and affiliates into Japanese yen are made
by applying the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet dates
for balance sheet items, except that the common stock, additional
paid-in capital and retained earnings accounts are translated at the
historical rates and the statements of income and retained earnings
are translated at average exchange rates.
(d) Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents in the consolidated statements of cash
flows are composed of cash on hand, bank deposits able to be with-
drawn on demand and short-term investments with an original maturity
of three months or less and which represent a minor risk of fluctua-
tion in value.
(e) Marketable Securities and Investment Securities
Marketable securities and investment securities are stated at cost
which is determined by the moving average method.
(f) Inventories
Inventories are valued principally on an average-cost basis.
(g) Property, Plant and Equipment Depreciation
Depreciation of property, plant and equipment for the Company and
domestic consolidated subsidiaries is computed using the declining
balance method except for depreciation of buildings acquired after
April 1, 1998, based on the estimated useful lives of assets which
are prescribed by Japanese income tax laws.
Depreciation of buildings acquired after April 1, 1998 is computed
using the straight-line method, based on the same estimated useful
lives as above. Depreciation of foreign subsidiaries is computed using
the straight-line method.
Ordinary maintenance and repairs are charged to income as
incurred. Major replacements and improvements are capitalized.
When properties are retired or otherwise disposed of, the property
and related accumulated depreciation accounts are relieved of the
applicable amounts and any differences are charged or credited
to income.
(h) Retirement Plans
Employees of the Company are, under normal circumstances, entitled
to a lump-sum retirement payment based upon the length of service
and current salary at the time of retirement.
The Company has funded pension plans with trust banks and insur-
ance companies to cover a portion of retirement benefits payable to
employees. It is the policy of the Company to provide for the “Reserve
for employees’ retirement allowances” in an amount equivalent to
the present value of the liability for such retirement benefits payable
to all eligible employees upon their voluntary retirement at the bal-
ance sheet dates, less the accumulated balance of fund assets
at such dates.
Under the plans, 50 per cent of the retirement benefits payable
to employees retiring at their mandatory retirement age is paid out
of the pension plans. The past service costs are being amortized over
a period of 12 years and 6 months.