Kia 2002 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2002 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
2002 KIA MO TO RS AN N UAL REPORT
5253
Financial Statements & Notes
Accrued severance benefits are approximately 56 percent and 55 percent funded as of December 31, 2002 and 2001, respectively, through an individual
severance insurance plan. Individual severance insurance deposits, in w hich the beneficiary is a respective employee, are presented as deduction from
accrued severance benefits.
Before April 1999, the Company and its employees paid 3 percent and 6 percent, respectively, of monthly pay (as defined) to the National Pension Fund
in accordance w ith the National Pension Law of Korea. The Company paid half of the employees’ 6 percent portion and is paid back at the termination
of service by offsetting the receivable against the severance payment. Such receivables, totalling 48,018 million ($40,002 thousand) and 51,078
million ($42,551 thousand) as of December 31, 2002 and 2001, respectively, are presented as a deduction from accrued severance benefits. Since April
1999, according to a revision in the National Pension Law , the Company and its employees each pay 4.5 percent of monthly pay to the Fund.
Stock Options
The Company granted stock options to employees and directors. The Company computes total compensation expense to stock options by the fair value
method using the option-pricing model. The compensation expense has been accounted for as a charge to current operations and a credit to capital
adjustment from the grant date using the straight-line method.
Derivative Instruments
All derivative instruments are accounted for at fair value w ith the valuation gain or loss recorded as an asset or liability. If the derivative instrument is not
part of a transaction qualifying as a hedge, the adjustment to fair value is reflected in current operations. The accounting for derivative transactions that
are part of a qualified hedge based both on the purpose of the transaction and on meeting the specified criteria for hedge accounting differs depending
on w hether the transaction is a fair value hedge or a cash flow hedge. Fair value hedge accounting is applied to a derivative instrument designated as
hedging the exposure to changes in the fair value of an asset or a liability or a firm commitment (hedged item) that is attributable to a particular risk.
The gain or loss both on the hedging derivative instruments and on the hedged item attributable to the hedged risk is reflected in current operations.
Cash flow hedge accounting is applied to a derivative instrument designated as hedging the exposure to variability in expected future cash flow s of an
asset or a liability or a forecasted transaction that is attributable to a particular risk. The effective portion of gain or loss on a derivative instrument desig-
nated as a cash flow hedge is recorded as a capital adjustment and the ineffective portion is recorded in current operations.
The effective portion of gain or loss recorded as a capital adjustment is reclassified to current earnings in the same period during w hich the hedged fore-
casted transaction affects earnings. If the hedged transaction results in the acquisition of an asset or the incurrence of a liability, the gain or loss in capi-
tal adjustment is added to or deducted from the asset or the liability.
Accounting for Foreign Currency Transactions and Translation
The Company maintains its accounts in Korea w on. Transactions in foreign currencies are recorded in Korean w on based on the prevailing rates of
exchange on the transaction date. M onetary accounts w ith balances denominated in foreign currencies are recorded and reported in the accompanying
financial statements at the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet dates. The balances have been translated using the Bank of Korea Basic Rate,
w hich w as 1,200.40 and 1,326.10 to US $1.00 at December 31, 2002 and 2001, respectively, and the translation loss and gain is reflected in cur-
rent operations.
NOTES TO NON-CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEM ENTS DECEM BER 31, 2002 AND 2001 NOTES TO NON-CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEM ENTS DECEM BER 31, 2002 AND 2001
Income Tax Expense
The Company recognizes deferred income taxes. Accordingly, income tax expense is determined by adding or deducting the total income tax and sur-
taxes to be paid for the current period and the changes in deferred income tax debits (credits). The difference betw een the income tax expense and the
amount of income tax show n in the current period' s tax return w ill be offset against the deferred income tax credits (debits), w hich w ill occur in subse-
quent periods.
Earnings Per Share
Basic ordinary income per common share and basic earnings per common share are computed by dividing ordinary income (after deduction for tax
effect) and net income, respectively, by the w eighted average number of common shares outstanding during the year. The number of shares used in
computing ordinary income per share and earnings per share is 367,993,115 and 387,672,624 in 2002 and 2001, respectively. Diluted ordinary income
per share and diluted earnings per share are computed by dividing ordinary income and net income, after addition for the effect of expenses related to
diluted securities on net income, by the number of the w eighted average number of common shares plus the number of dilutive potential common
shares. As the Company has not issued any diluted securities and the stock options have no dilutive effect on basic ordinary income per share and basic
earnings per share in 2002 and 2001, basic ordinary income per share and basic earnings per share are equal to diluted ordinary income per share and
diluted earnings per share, respectively.
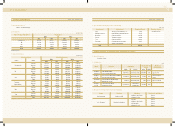
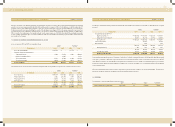
3. INVENTORIES
Inventories as of December 31, 2002 and 2001 consist of the follow ing:
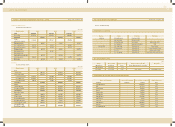
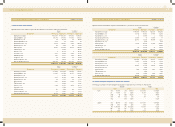
4. M ARKETABLE SECURITIES AND INVESTMENT SECURITIES
(1) M arketable securities as of December 31, 2002 and 2001 are stated at fair value and consist of debt securities amounting to 19,565
million ($16,299 thousand) and 30,620 million ($25,508 thousand), respectively.
As of December 31, 2002, the Company has pledged part of its marketable securities amounting to 8,790 million ($7,323 thousand)
as collateral for certain borrow ings.
Finished goods and merchandise 195,570 193,775 162,921 161,425
Semi-finished goods and w ork in process 116,130 88,076 96,743 73,372
Raw materials and supplies 126,631 106,628 105,491 88,827
M aterials in transit 46,687 31,938 38,892 26,607
485,018 420,417 404,047 350,231
2002 2001 2002 2001
Korean won U.S. dollars(Note 2)
(in millions) (in thousands)