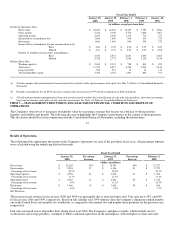
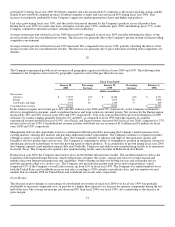
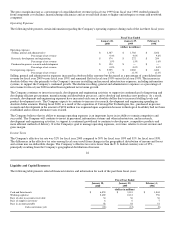
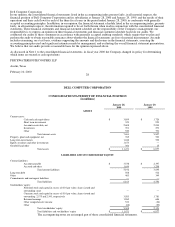
Dell 1999 Annual Report Download - page 24
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 24 of the 1999 Dell annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
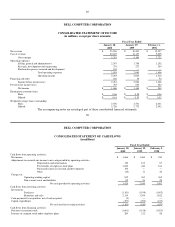
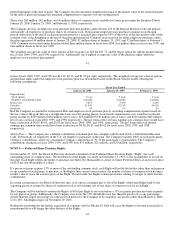
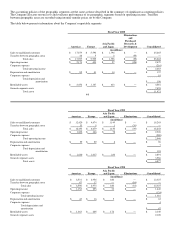
government, healthcare and education accounts, as well as small-to-medium businesses and individuals and to some extent value-
added resellers. The Company conducts operations worldwide through wholly owned subsidiaries; such operations are primarily
concentrated in the North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific and Japan regions.
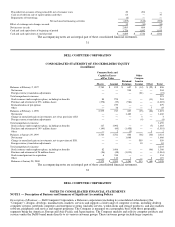
Fiscal Year — During fiscal year 1999, the Company changed its fiscal year from the 52 or 53 week period ending on the Sunday
nearest January 31 to the Friday nearest January 31. The change in fiscal year had no material effect on the Company's consolidated
financial statements.
Principles of Consolidation — The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally
accepted accounting principles and include the accounts of the Company. All significant intercompany transactions and balances have
been eliminated.
Use of Estimates — The preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles requires the
use of management's estimates. These estimates are subjective in nature and involve judgements that affect the reported amounts of
assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at fiscal year end and the reported amounts of revenues and
expenses during the fiscal year. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
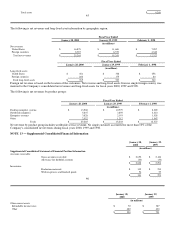
Cash and Cash Equivalents — During fiscal year 2000, the Company changed the method of classifying cash equivalents and has
restated prior year balances to reflect the change. All highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less at date
of purchase are carried at cost and considered to be cash equivalents. These investments were previously classified as marketable
securities. All other investments not considered to be a cash equivalent are now separately categorized as investments.
Investments — The Company's investments are classified as available-for-sale securities and are reported at fair value. Unrealized
gains and losses are reported, net of taxes, as a component of stockholders' equity. Unrealized losses are charged against income when
a decline in fair value is determined to be other than temporary. The specific identification method is used to determine the cost of
securities sold. Realized gains and losses on investments are included in Financing and Other when realized.
Inventories — Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market with cost being determined on a first-in, first-out basis.
Property, Plant and Equipment — Property, plant and equipment are carried at depreciated cost. Depreciation is provided using the
straight-line method over the estimated economic lives of the assets, which range from 10 to 30 years for buildings and two to five
years for all other assets. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of five years or the lease term.
Goodwill and Other Intangibles — Amortization of goodwill and other intangibles is charged to income on a straight-line basis over
the periods estimated to benefit, ranging from three to eight years. The Company periodically performs reviews to evaluate the
recoverability of goodwill and
33
other intangibles and takes into account events or circumstances that warrant revised estimates of useful lives or that indicate that an
impairment exists.
Foreign Currency Translation — The majority of the Company's international sales are made by international subsidiaries which have
the U.S. dollar as their functional currency. International subsidiaries which have the U.S. dollar as the functional currency are
remeasured into U.S. dollars using current rates of exchange for monetary assets and liabilities and historical rates of exchange for
nonmonetary assets. Gains and losses from remeasurement are included in Financing and Other. The Company's subsidiaries that do
not have the U.S. dollar as their functional currency translate assets and liabilities at current rates of exchange in effect at the balance
sheet date. The resulting gains and losses from translation are included as a component of stockholders' equity. Items of revenue and
expense for the Company's international subsidiaries are translated using the monthly average exchange rates in effect for the period in
which the items occur.
Foreign Currency Hedging Instruments — The Company enters into foreign currency exchange contracts to hedge its foreign
currency risks. These contracts are designated at inception as a hedge and measured for effectiveness both at inception and on an
ongoing basis. Realized and unrealized gains or losses and premiums paid on foreign currency purchased option contracts that are
designated and effective as hedges of probable anticipated, but not firmly committed, foreign currency transactions are deferred and
recognized in income as a component of net revenue, cost of revenue and/or operating expenses in the same period as the hedged
transaction. Forward contracts designated as hedges of probable anticipated or firmly committed transactions are accounted for on a
mark-to-market basis, with realized and unrealized gains or losses recognized in the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Income.
Equity Instruments Indexed to the Company's Common Stock — Proceeds received upon the sale of equity instruments and amounts
paid upon the purchase of equity instruments are recorded as a component of stockholders' equity. Subsequent changes in the fair
value of the equity instrument contracts are not recognized. If the contracts are ultimately settled in cash, the amount of cash paid or
received is recorded as a component of stockholders' equity.
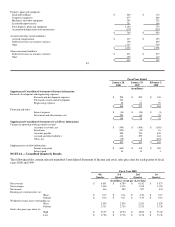
Revenue Recognition — Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers. Provision is made for an estimate of product
returns and doubtful accounts and is based on historical experience. Revenue from separately priced service and extended warranty
programs is deferred and recognized over the respective service or extended warranty period.
Warranty and Other Post-sales Support Programs — The Company provides currently for the estimated costs that may be incurred
under its initial warranty and other post-sales support programs.