Cisco 2010 Annual Report Download - page 40
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 40 of the 2010 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
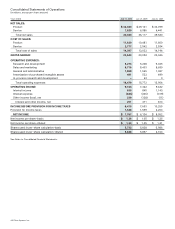
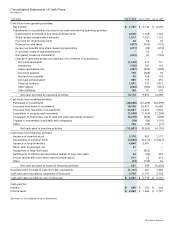
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
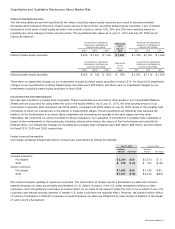
Approximately 70% of our operating expenses are U.S.-dollar denominated. Foreign currency fluctuations, net of hedging,
increased our operating expenses, categorized as research and development, sales and marketing, and general and administrative,
by approximately 0.2% in fiscal 2010 compared with fiscal 2009 and decreased our operating expenses by approximately 1.8% in
fiscal 2009 compared with fiscal 2008. To reduce variability in operating expenses and service cost of sales caused by non-U.S.-
dollar denominated operating expenses and costs, we hedge certain foreign currency forecasted transactions with currency
options and forward contracts. These hedging programs are not designed to provide foreign currency protection over long time
horizons. In designing a specific hedging approach, we consider several factors, including offsetting exposures, significance of
exposures, costs associated with entering into a particular hedge instrument, and potential effectiveness of the hedge. The gains
and losses on foreign exchange contracts mitigate the effect of currency movements on our operating expenses and service cost
of sales.
We also enter into foreign exchange forward and option contracts to reduce the short-term effects of foreign currency
fluctuations on receivables, investments, and payables, denominated in currencies other than the functional currencies of the
entities. The market risks associated with these foreign currency receivables, investments, and payables relate primarily to
variances from our forecasted foreign currency transactions and balances. Our forward and option contracts generally have the
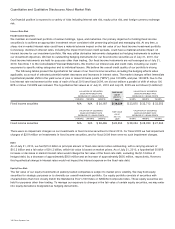
following maturities:
Maturities
Forward and option contracts—forecasted transactions related to operating expenses and service cost of sales Up to 18 months
Forward contracts—current assets and liabilities Up to 3 months
Forward contracts—net investments in foreign subsidiaries Up to 6 months
Forward contracts—long-term customer financings Up to 2 years
Forward contracts—investments Up to 2 years
We do not enter into foreign exchange forward or option contracts for trading purposes.
38 Cisco Systems, Inc.