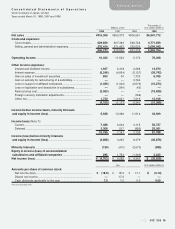
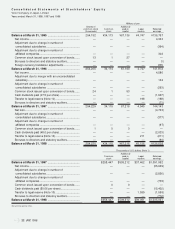
JVC 1998 Annual Report Download - page 29
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 29 of the 1998 JVC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
JVC 1998 27
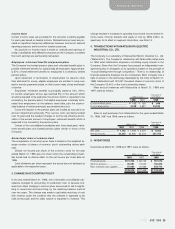
The aggregate annual maturities of long-term debt at March 31,
1998, were as follows:
Thousands of
Year ending March 31, Millions of yen U.S. dollars
1999 ................................................... ¥20,431 $154,780
2000 ................................................... 18,233 138,129
2001 ................................................... 30 227
2002 ................................................... 591 4,477
2003 ................................................... 20,029 151,735
Thereafter............................................ 32,012 242,515
........................................................... ¥91,326 $691,863
9. PLEDGED ASSETS
The following assets were pledged as collateral for long-term debt and
accrued expenses at March 31, 1998:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
Investments......................................... ¥ 8 $ 61
Machinery and equipment ................... 561 4,250
Finished goods.................................... 166 1,257
........................................................... ¥735 $5,568
10. LEGAL RESERVE AND RETAINED EARNINGS
The Commercial Code of Japan provides that an amount equal to at
least 10% of cash dividends and bonuses to directors and statutory au-
ditors for each fiscal year shall be appropriated and set aside as a legal
reserve until such reserve equals 25% of common stock. This legal re-
serve is not available for dividends, but may be used to reduce a deficit
by resolution of a stockholders’ meeting or may be capitalized by reso-
lution of the Board of Directors.
Consolidated retained earnings included legal reserves and re-
tained earnings of consolidated subsidiaries, which were earned after
acquisition.
11. CONTINGENT LIABILITIES
The contingent liabilities of the Company and its consolidated sub-
sidiaries at March 31, 1998, were as follows:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
As endorser of export bills
discounted with banks........................ ¥ 4,988 $ 37,788
As guarantor for loans of
employees.......................................... 17,579 133,174
........................................................... ¥22,567 $170,962
12. FORWARD FOREIGN EXCHANGE CONTRACTS —
12. THE COMPANY ONLY
At March 31, 1998, the Company had contracts to sell various foreign
currencies, mainly U.S. dollars. The aggregate contract amount and
fair value of forward foreign exchange contracts equivalent in Japanese
yen at March 31, 1998, were ¥54,613 million and ¥56,047 million,
respectively.
The Company also had contracts to purchase various foreign
currencies, mainly U.S. dollars. The aggregate contract amount and
fair value of forward foreign exchange contracts equivalent in Japanese
yen at March 31, 1998, were ¥32,119 million and ¥33,550 million,
respectively.
The forward contracts on the foreign currency receivables and
payables translated into Japanese yen at the forward exchange rates
on the financial statements were not included in the above amounts.
13. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On June 26, 1998, the Company’s stockholders authorized (1) payment
of a cash dividend to stockholders of record on March 31, 1998 of ¥3.5
($0.03) per share, totaling ¥890 million ($6,742 thousand), (2) payment
of bonuses to directors and statutory auditors of ¥72 million ($545
thousand) and (3) transfer to legal reserve of ¥96 million ($727 thou-
sand) from retained earnings.
14. SEGMENT INFORMATION
The Company and its consolidated subsidiaries operate primarily in the
audiovisual and information-related business and entertainment busi-
ness. As explained in Note 2, the amounts for 1997 are based on
revised accounting standards. Assuming the amounts for 1996 are
translated into Japanese yen based on the same manner as those for
1997, operating income (loss) of the Audiovisual and information-
related business segment and the Entertainment business segment
would increase by ¥829 million and ¥435 million, respectively. Also, as-
sets of the Audiovisual and information-related business segment and
the Entertainment business segment would decrease by ¥172 million
and ¥787 million, respectively.
As explained in Note 3, a consolidated subsidiary changed its ac-
counting for the production cost of karaoke software in 1996. As a re-
sult, operating expenses of Entertainment business segment decreased
by ¥863 million and operating income increased by the same amount
for the year ended March 31, 1996.
Financial Section