Suzuki 2007 Annual Report Download - page 35
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 35 of the 2007 Suzuki annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SUZUKI MOTOR CORPORATION
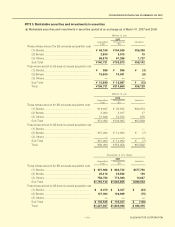
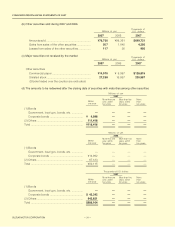
(f) Marketable securities, investment in securities
The Company and its subsidiaries hold securities of financial institutions and of our suppliers. These are
subject to the risk of price fluctuations and under certain market conditions, we may have to conduct a review of
their valuations and downgrade our assessments accordingly, based on the reasonable accounting standards. If
the stock market falls, we may incur significant valuation losses of marketable securities.
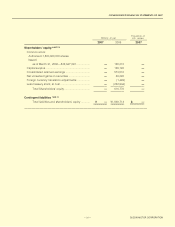
Securities have to be classified into four categories: trading securities; held-to-maturity debt securities;
investments of the Company in equity securities issued by unconsolidated subsidiaries and affiliates; and other
securities.
According to this classification, securities held by the Company and its subsidiaries are other securities. Other
securities for which market quotations are available are stated at fair value by the closing date’s market value
method. Unrealized gains or losses are included in a component of net assets at a net-of-tax amount, and gains
or losses from sales of securities are recognized on cost determined by the moving average method.
Other securities for which market quotations are unavailable are stated at cost by a moving average method.
(g) Hedge accounting
Gains or losses arising from changes in fair value of the derivatives designated as “hedging instruments” are
deferred as an asset or liability and included in net profit or loss in the same period during which the gains and
losses on the hedged items or transactions are recognized.
The derivatives designated as hedging instruments by the Company and its subsidiaries are principally
interest swaps and forward exchange contracts.The related hedged items are trade accounts receivable and
investments in securities.
The Company and its subsidiaries have a policy to utilize the above hedging instruments in order to reduce
our exposure to the risk of interest rate and foreign exchange fluctuation. Thus, our purchases of the hedging
instruments are limited to, at maximum, the amounts of the hedged items. The Company and its subsidiaries
evaluate effectiveness of its hedging activities by reference to the accumulated gains or losses on the hedging
instruments and the related hedged items from the commencement of the hedges.
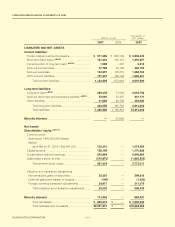
(h) Foreign currency translation
All monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies, whether long-term or short-term are
translated into Japanese yen at the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet date. Resulting gains and
losses are included in net profit or loss for the period.
Assets and liabilities of the foreign subsidiaries and affiliates are translated into Japanese yen at the exchange
rates prevailing at the balance sheet date.
The components of net assets are translated into Japanese yen at their historical rates. Profit and loss accounts
for the year are translated into Japanese yen using the average exchange rate during the year, or alternatively, using
the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet date.Differences in yen amounts arising from the use of different
rates are presented as “foreign currency translation adjustments” in the net assets.
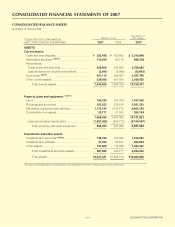
(i) Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market value, cost being determined principally by the periodic
average method.
(j) Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is principally computed by the declining-
balance method based on estimated useful lives of the assets (mainly 3-75 years).
Provision for additional depreciation to certain assets is made to reflect the use of machinery and equipment in
excess of normal production schedules, a substantial portion of which is, however, not tax deductible.
Maintenance and repairs, including minor renewals and improvements, are charged to income as incurred.
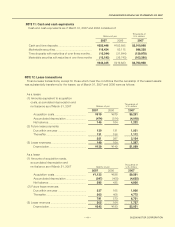
(k) Leases
Finance lease transactions, except for those which meet the conditions that the ownership of the lease assets
is substantially transferred to the lessee, are accounted for on a basis similar to ordinary rental transactions.
(l) Income taxes
The provision for income taxes is computed based on the income before income taxes included in
Consolidated Statements of Income. The assets and liability approach is adopted to recognize deferred tax
assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the carrying
amounts and the tax bases of assets and liabilities.
In making a valuation for the possibility of collection of deferred tax assets, the Company and its subsidiaries
estimate our future taxable income reasonably. If the estimated amount of future taxable income decrease,
deferred tax assets may decrease and income taxes expenses may be posted.
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF 2007
35