Navy Federal Credit Union 2008 Annual Report Download - page 9
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 9 of the 2008 Navy Federal Credit Union annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
derivative financial instruments at December 31,
2008 and 2007: mortgage loan commitments to
members at specified interest rates and forward sales
contracts to offset the risk of making the mortgage
loan commitments at specified interest rates. See
Note 7 for details.
Pension Accounting and Retirement
Benefit Plans
Navy Federal has defined benefit pension plans,
401(k) and 457(b) savings plans and a non-qualified
supplemental retirement plan. Navy Federal also
provides a contributory group medical plan for retired
employees. Navy Federal accounts for its defined
benefit pension plans in accordance with SFAS
No. 87, Employers’ Accounting for Pensions. Non-
pension postretirement benefits are accounted for
in accordance with SFAS No. 106, Employers’
Accounting for Postretirement Benefits Other Than
Pensions. In 2004, Navy Federal adopted SFAS No.
132, Employers’ Disclosures about Pensions and
Other Postretirement Benefits. As of December 31,
2007, Navy Federal adopted SFAS No. 158, Employ-
ers’ Accounting for Defined Benefit Pension and
Other Postretirement Plans. See Note 13 for more
information.
Income Taxes
Pursuant to the Federal Credit Union Act, Navy Federal
is exempt from the payment of federal and state
income taxes. NFFG is a limited liability corporation
and thus, is an entity “disregarded for federal tax
purposes” under Internal Revenue Service Revenue
Ruling. Consequently, it did not incur federal or state
income tax liability.
Dividends
Dividend rates on members’ accounts are set by
the Board of Directors and dividends are charged
to operations. Dividends on all share products are
paid monthly.
Reclassifications
Certain amounts in the prior year have been
reclassified to conform to current year presentation.
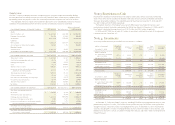
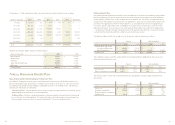
Note 2: Restatement of 2007
Financial Statements
Navy Federal chose to restate its 2007 financial
statements for adjustments related to deferred
loan fees under Statement of Financial Accounting
Standards No. 91, Accounting for Nonrefundable
Fees and Costs Associated with Originating and
Acquiring Loan and Initial Direct Costs of Leases
(SFAS No. 91), certain loan sales under Statement
of Financial Accounting Standards No. 140, Account-
ing for Transfers and Servicing of Financial Assets
and Extinguishments of Liabilities (SFAS No. 140)
and property leases under Statement of Financial
Accounting Standards No. 13, Accounting for
Leases (SFAS No. 13) as further described below:
SFAS No. 91 Adjustment
SFAS No. 91 establishes the accounting for nonre-
fundable fees and costs associated with lending,
committing to lend, or purchasing a loan or group
of loans. Prior to 2008, Navy Federal did not apply
SFAS No. 91 as the impact was not material. Navy
Federal implemented SFAS No. 91 in 2008 and
chose to restate 2007 in order to show comparative
statements for the years ended 2008 and 2007.
SFAS No.140 Adjustment
Navy Federal sold certain mortgage loans to the
Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae)
and accounted for these loans as sales transactions
under SFAS No. 140. In 2008, it was determined
that these transactions should have been treated as
secured borrowings. Therefore, Navy Federal restated
its 2007 financial statements to reflect the impact of
accounting for these transactions as secured borrow-
ings. The contract with Fannie Mae was amended
in August 2008, and accordingly, the loans were
treated as sales at that time. A recourse obligation
of $1.4 million was established in 2008 which was
reflected in Other Liabilities.
for loan and lease products are deferred and
amortized over the life of the loans under SFAS No.
91, Accounting for Nonrefundable Fees and Costs
Associated With Originating or Acquiring Loans and
Initial Direct Costs of Leases.
Navy Federal currently uses the direct financing
method to account for all automobile leases. Under
this method, lease contract receivables are the total
minimum lease payments plus residual value of
the leased automobiles, net of unearned interest
revenue. Interest revenue is recognized monthly
on receipt of rental payment.
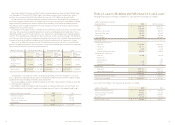
Allowance for Loan Losses
Navy Federal accrues estimated losses in accordance
with SFAS No. 5, Accounting for Contingencies. The
allowance for loan losses is established through a
provision for loan losses charged to expense. Loan
principal is charged against the allowance for loan
losses when management believes that the collectibil-
ity of the amount is unlikely; subsequent recoveries
are credited to the allowance for loan losses. Navy
Federal’s loan portfolio consists mainly of large groups
of smaller balance homogeneous loans that are
collectively evaluated for impairment. The allowance
for loan losses is maintained at a level that, in man-
agement’s judgment, is sufficient to absorb losses
inherent in the portfolio, based on evaluations of the
collectibility of loans and prior loan loss experience.
The evaluations take into consideration such factors
as changes in the value of loans outstanding, prior
history of charge-offs and recoveries, overall delin-
quency and delinquencies by loan product, and
current economic conditions and trends that may
affect a borrower’s ability to pay. The allowance
for loan and lease losses is reviewed on a monthly
basis and the provision that is charged to expense
is adjusted accordingly.
Fixed Assets
Land is carried at cost. Building, leasehold improve-
ments, furniture, fixtures, and equipment are carried
at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortiza-
tion. Buildings, furniture, fixtures and equipment are
depreciated using the straight-line method over their
estimated useful lives. The cost of leasehold improve-
ments is amortized over the lease term or the useful
life of the improvement, whichever is shorter.
Navy Federal uses the straight-line method to
account for its operating leases. Under this method,
Navy Federal divides the total contractual rent by the
total term of the lease. The average monthly rent is
recorded as rent expense and the remaining rent
amount is deferred.
NCUSIF Deposit
The deposit in the National Credit Union Share
Insurance Fund (NCUSIF) is in accordance with the
Federal Credit Union Act and the National Credit
Union Administration (NCUA) regulations, which
require the maintenance of a deposit by each insured
credit union in an amount equal to one percent of
its insured shares. The deposit would be refunded to
Navy Federal if its insurance coverage is terminated,
it converts to insurance coverage from another
source, or the operations of the fund are transferred
from the NCUA Board.
See Note 21 for additional information about the
NCUSIF deposit.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of purchase price
over the fair value of net assets acquired in business
combinations. SFAS No. 142, Goodwill and Other
Intangible Assets, provides that intangible assets
with finite useful lives be amortized and that goodwill
and intangible assets with indefinite lives not be
amortized, but rather be tested at least annually for
impairment. Navy Federal tests goodwill for impair-
ment quarterly in compliance with SFAS No. 142.
Impairment exists when the carrying amount of
the goodwill exceeds its implied fair value.
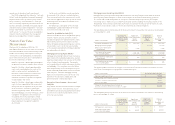
Derivative Financial Instruments
In compliance with SFAS No. 133, Accounting for
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, all
derivative financial instruments are recognized on the
balance sheet at fair value. Changes in the fair value
of derivative financial instruments are recorded in
current earnings. Navy Federal owned the following
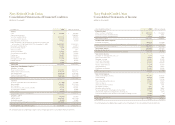
NAVY FEDERAL CREDIT UNION
8 9
2008 FINANCIAL SECTION
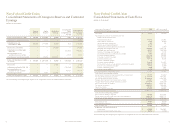
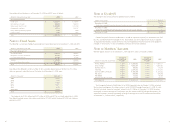
Useful Life
Buildings 24 to 40 years
Furniture and equipment 5 to 7 years
Computer equipment 2 to 5 years
Computer software 5 years