Sharp 2011 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2011 Sharp annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
57
Annual Report 2011
Financial Section
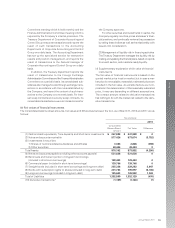
(Note 1) Methods of Calculating the Fair Value of Financial
Instruments and Matters Related to Securities and
Derivative Transactions
(1) Cash and cash equivalents, Time deposits, and
Short-term investments
The fair value of time deposits and Short-term invest-
ments approximates their book value, due to their
short maturity periods.
(2) Notes and accounts receivable
The fair value of notes and accounts receivable due
within a year, approximates their book value. The
fair value of notes and accounts receivable with
long maturity periods is discounted using a rate
which reflects both the period until maturity and
credit risk.
(3) Investments in securities
The fair value of investments in securities is based
on average quoted market prices for the last month
of the fiscal year.
(4) Notes and accounts payable (excluding other
accounts payable)
The fair value of notes and accounts payable
(excluding other accounts payable) approximates
their book value, due to their short maturity peri-
ods.
(5) Bank loans and current portion of long-term bor-
rowings (included in short-term borrowings)
The fair value of bank loans and current portion of
long-term borrowings approximates their book
value, due to their short maturity periods.
(6) Commercial paper (included in short-term borrow-
ings)
The fair value of commercial paper approximates
their book value, due to their short maturity periods.
(7) Straight bonds (included in short-term borrowings
and long-term debt)
The fair value of marketable straight bonds is deter-
mined by the quoted market price. The fair value
of non-marketable straight bonds is based on quot-
ed prices from financial institutions.
(8) Bonds with subscription rights to shares (included
in long-term debt)
The fair value of marketable bonds with subscrip-
tion rights to shares is determined by the quoted
market prices. The fair value of non-marketable
bonds with subscription rights to shares is based
on quoted prices from financial institutions.
(9) Long-term borrowings (included in long-term debt)
The fair value of long-term borrowings is deter-
mined by the total amount of the principal and inter-
est using the rate which would apply if similar
borrowings were newly made.
(10) Derivative transactions
The fair value of currency swap contracts and inter-
est swap contracts is based on quoted prices from
financial institutions. The fair value of forward
exchange contracts are based on forward exchange
rate.
(Note 2) As unlisted stocks ¥39,487 million as of March 31,
2010 and ¥36,567 million ($445,939 thousand) as
of March 31, 2011 and equity ¥371 million as of
March 31, 2010 and ¥8,477 million ($103,378 thou-
sand) as of March 31, 2011 have no quoted market
price and as it is not possible to accurately estimate
future cash flows, it is very difficult to determine
their fair value reasonably. Therefore, they are not
included in “(3) Investments in securities.”
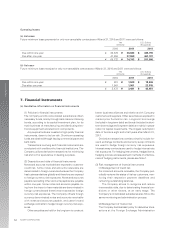
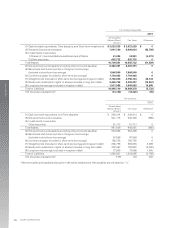
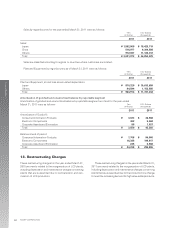
(Note 3) Maturity analysis for Cash and cash equivalents, Time deposits, and Short-term investments, and Notes and
accounts receivable.
Due in one
year or less
2011
Cash and cash equivalents, Time deposits, and Short-term investments
Notes and accounts receivable
Total
Yen (millions)
Due after
one year
¥—
49,323
¥ 49,323
¥ 247,888
528,103
¥ 775,991
Due in one
year or less
2011
Cash and cash equivalents, Time deposits, and Short-term investments
Notes and accounts receivable
Total
U.S. Dollars (thousands)
Due after
one year
$—
601,500
$ 601,500
$ 3,023,025
6,440,280
$ 9,463,305