Omron 2009 Annual Report Download - page 5
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 5 of the 2009 Omron annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
3
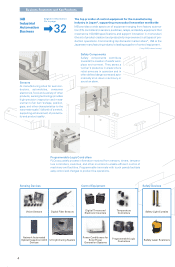
[1] Micromachining
Integrated circuit construction is typically two dimensional. Omron’s micromachining technology employs
micro electrical mechanical systems (MEMS) technology to enable three dimensional construction on a
micrometer scale for semiconductors. This technology enables production of the world’s smallest radio
frequency relays and ultra-small gas and fluid pressure sensors.
[2] Microphotonics
Microphotonics is a light wave control technology based on reflected and lenticular optics, allowing
greater miniaturization and integration by fabricating various optical component functions (brightness,
speed, energy saving, etc.) on a single substrate as with IC and LSIs. Microphotonics technology realizes
low-cost optical transmissions and offers potential for revolutionary devices using high-brightness LEDs
and other technologies.
[3] Image Sensing
Image sensing technology mechanically recognizes the movement of an object, such as a human face, by
detecting the transmission or reflection of light waves and generates detailed data on the object. This
technology is used for a diverse range of applications, including quality inspection, safety in driving, and in
security systems.
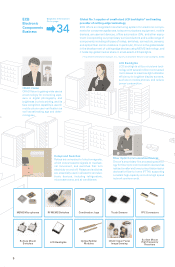
[4] Knowledge Information Control Technology
Omron possesses numerous patents in Japan for “fuzzy logic” technology resulting from its research on the theory of human
behavior based on know-how and intelligence. By integrating an algorithm of human problem-solving processes into a machine-
controlling device, the machine can learn and make decisions.
Japan
Subsidiaries 46
Affiliates 13
*Includes direct exports
Asia-Pacific
Subsidiaries 23
Affiliates 2
Greater China
Subsidiaries 25
Affiliates 2
Europe
Subsidiaries 40
Affiliates 1
Regional Headquarters
North America
Subsidiaries 28
08
328.1
06 07
0806 07
08
80.4
06 07
40.4
08
75.2
06 07
08
103.1
06 07
Sales Breakdown by Region
(Billions of yen)
Japan
*Includes direct exports
52%
North America
13%
Other Asia
6%
Greater
China
12%
Europe
16%
Sales Breakdown by Region
Net Sales
627.2 billion
FY2008
Global Network
To meet customer demand, ‘what they want when they want it’, Omron has established a global network and
a closely linked service system covering our operating regions of Japan, North America, Europe, Greater
China, and Asia Pacific. Omron provides fast and efficient support to its business partners worldwide through
its comprehensive support system, from development to production, distribution, and maintenance.
Core Technologies Supporting Sensing and Control
4 mm
3 mm