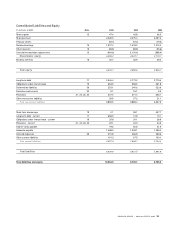
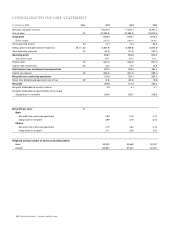
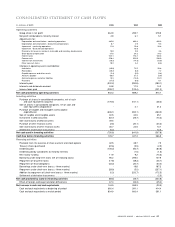
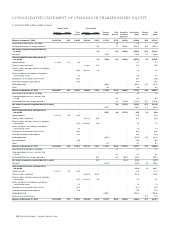
Food Lion 2005 Annual Report Download - page 47
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 47 of the 2005 Food Lion annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Foreign currency transactions are recognized initially at exchange rates prevail-
ing at the date of the transaction. Subsequently monetary assets and liabilities
denominated in foreign currencies are translated at the balance sheet currency
rate. Gains and losses resulting from the settlement of foreign currency transac-
tions and from the translation of monetary assets and liabilities denominated in
foreign currencies are included in the income statement. Exchange differences
arising on the retranslation of non-monetary items carried at fair value are includ-
ed in the income statement except for differences arising on the retranslation of
non-monetary items in respect of which gains and losses are recognized directly
in equity. For such non-monetary items, any exchange component of that gain or
loss is also recognized directly in equity.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the Delhaize Group’s consolidated financial statements in
conformity with IFRS requires the Group to use estimates and make assumptions
that may affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures
of contingent assets and liabilities and the reported amounts of revenue and
expense. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Estimates are par-
ticularly important to, but not limited to, determining the adequacy of provisions
for closed stores, self-insurance obligations and obligations related to defined
benefit plans and for assessing assets for impairment.
Goodwill
The purchase method of accounting is used to account for acquisitions of subsidi-
aries by the Group. The cost of an acquisition is measured as the fair value of the
assets given, equity instruments issued and liabilities and contingent liabilities
incurred or assumed at the date of acquisition, plus costs directly attributable
to the acquisition. Identifiable assets acquired and liabilities and contingent
liabilities assumed in a business combination are measured initially at their fair
values at the acquisition date, irrespective of the extent of any minority interest.
The excess of the cost of acquisition over the fair value of the Group’s share of the
identifiable net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. If the cost of acquisition
is less than the fair value of the net assets of the subsidiary acquired, the differ-
ence is recognized directly in the income statement.
Goodwill is not amortized but reviewed for impairment annually and when there is
an indication that goodwill may be impaired. For the purpose of testing goodwill
for impairment, goodwill is allocated to the lowest level at which the goodwill
is monitored for internal management purposes. Any impairment is recognized
immediately in the income statement and cannot be subsequently reversed.
Consistent with all other assets and liabilities, goodwill arising on the acquisi-
tion of a foreign operation is treated as an asset of the foreign operation and is
carried in the functional currency of the subsidiary and converted at the closing
exchange rate into EUR.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets include trade names and favorable lease rights that have been
acquired in business combinations, and computer software, various licenses and
prescription files. Intangible assets are stated at cost less accumulated deprecia-
tion and accumulated impairment losses. Intangible assets with finite lives are
amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives. The useful
lives of intangible assets with finite lives are as follows:
• Prescription files 15 years
• Favorable lease rights Lease term
• Computer software 3 to 5 years
Intangible assets with indefinite useful lives are not amortized but tested for
impairment annually and when there is an indication that the asset may be
impaired. The Group believes that trade names have indefinite lives because
they contribute directly to the Group’s cash flows as a result of recognition by the
customer of each banner’s characteristics in the marketplace. There are no legal,
regulatory, contractual, competitive, economic or other factors that limit the use-
ful life of the trade names.
Property, Plant and Equipment and Investment Property
Property, plant and equipment and investment property are stated at cost less
accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses. Depreciation is
calculated using the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives
of the related assets. Finance lease assets and leasehold improvements are
depreciated over the lesser of the expected useful life of similar owned assets
or the relevant lease term. Land is not depreciated. Useful lives of tangible fixed
assets are as follows:
• Buildings 33 to 40 years
• Plant, machinery and equipment 3 to 14 years
• Furnitures, vehicles and other tangible fixed assets 5 to 10 years
Non-current Assets Held for Sale
Non-current assets and disposal groups are classified as held for sale if their
carrying amount will be recovered through a sale transaction rather than through
continuing use. This condition is regarded as met only when the sale is highly
probable and the asset (or disposal group) is available for immediate sale in
its present condition. Management must be committed to the sale and the sale
should be expected to qualify for recognition as a completed sale within one year
from the date of classification. Non-current assets held for sale are measured
at the lower of the asset’s previously carrying amount or fair value less costs
to sell.
Borrowing Costs
Borrowing costs attributable to the construction or production of qualifying assets
are capitalized.
Leases
Leases are classified as finance leases when the terms of the lease transfer
substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership to the Group. All other leases
are classified as operating leases.
Assets held under finance leases are recognized as assets at the lower of fair
value or present value of the minimum lease payments at the inception of the
lease. The corresponding liability to the lessor is included in the balance sheet as
a finance lease obligation. Lease payments are allocated between finance costs
and a reduction of the lease obligation to achieve a constant rate of interest over
the lease term.
Rents paid on operating leases are charged to income on a straight-line basis over
the term of the lease. Benefits received and receivable as an incentive to enter
into an operating lease are spread over the relevant lease term on a straight-line
basis as a reduction in rent expense.
Impairment of Assets
The Group tests assets for impairment whenever events or circumstances indicate
that impairment may exist. Goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives
are tested for impairment at least annually. The Group has identified a store as
a cash generating unit. Stores for which there is potential impairment are tested
for impairment by comparing the carrying value of the assets to the higher of
their value in use (projected discounted cash flows) or fair value less costs to
sell. If impairment exists, the assets are written down to their recoverable amount
(higher of value in use or fair value less cost to sell). If impairment is no longer
justified in future periods due to a recovery in assets’ fair value or value in use,
the impairment is reversed except for goodwill.
DELHAIZE GROUP / ANNUAL REPORT 200 5 45