Konica Minolta 1999 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 1999 Konica Minolta annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
24 KONICA
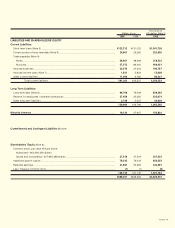
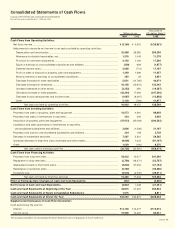
Transaction balances as of March 31, 1999 and 1998 are as follows:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
1999 1998 1999
Trade receivables ....................... ¥6,019 ¥11,167 $49,336
Trade payables........................... 6,104 8,214 50,033
5. Short-Term Loans
Short-term loans consist principally of bank borrowings. The average
interest rates on these loans as of March 31, 1999 and 1998 were 4.2
per cent and 4.9 per cent per annum, respectively.
6. Long-Term Debt
Long-term debt as of March 31, 1999 and 1998 is summarized as
follows:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
1999 1998 1999
1.6% to 3.2% Japanese yen
unsecured debentures,
due 1999 to 2008 ................. ¥ 57,750 ¥ 56,632 $ 473,361
1.0% to 5.7% mortgage
loans from banks,
due 1999 to 2005 ................. 2,920 2,390 23,934
6.6% to 7.8% mortgage
or secured loans from
government-sponsored
banks and agencies,
due 1999 to 2001 ................. 941 1,571 7,713
0.6% to 8.7% unsecured
loans from banks and
government-sponsored
banks and agencies,
due 1999 to 2008 ................. 57,036 37,296 467,508
Obligations under capital
leases, due 1999 to 2006..... 7,023 5,380 57,566
............................................... 125,670 103,269 1,030,082
Less: Current portion included
in current liabilities ............... (26,901) (24,260) (220,500
............................................... ¥ 98,769 ¥ 79,009 $ 809,582
At March 31, 1999, property, plant and equipment amounting to
¥5,695 million (US$46,680 thousand) at net book value was pledged
as collateral for long-term debt of ¥4,685 million (US$38,402 thousand).
As is customary in Japan, long-term and short-term bank loans are
made under general agreements which provide that additional security
and guarantees for present and future indebtedness will be given at
the request of the bank and that any collateral so furnished will be
applicable to all indebtedness due to that bank. In addition, the agree-
ments provide that the bank has the right to offset cash deposited
against any long-term or short-term debt that becomes due and, in
case of default and/or other specified events, against all other debt
payable to the bank.
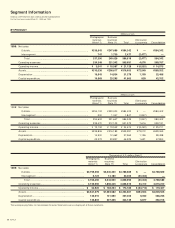
The aggregate annual maturities of long-term debt as of March 31,
1999 are as follows:
Thousands of
Years ending March 31 Millions of yen U.S. dollars
1999........................................................ ¥ 26,902 $ 220,508
2000........................................................ 21,278 174,410
2001........................................................ 22,091 181,074
2002........................................................ 14,679 120,320
2003 and thereafter ................................ 40,720 333,770
................................................................ ¥125,670 $1,030,082
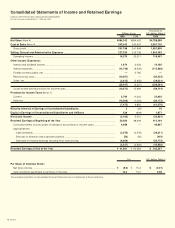
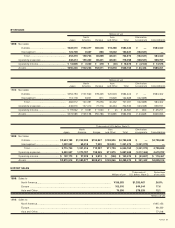
7. Income Taxes
The Company is subject to a number of different taxes in Japan,
based on income, which in the aggregate indicate statutory tax rates
of approximately 47.7 per cent and 51.4 per cent in 1999 and 1998,
respectively. The following is a reconciliation between the statutory
tax rate and the Company’s effective tax rate:
1999
Statutory tax rate .................................................................... 47.7%
Tax effect on loss of a consolidated subsidiary
previously not recognized................................................. 122.7
Valuation allowance............................................................ (16.1)
Effect of tax rate change..................................................... (40.8)
Inventories, etc. ................................................................. (35.5)
Other, net............................................................................ (7.8)
Effective tax rate..................................................................... 70.2
The components of deferred tax assets in the amount of ¥5,688 mil-
lion (US$46,623 thousand) included in “Current Assets” and ¥21,036
million (US$172,426 thousand) included in “Investments and Other
Assets” as of March 31, 1999 are as follows:
Millions of yen
Gross deferred tax assets:
Tax effect on loss of a consolidated subsidiary
previously not recognized .......................................... ¥12,814
Tax loss carryforward................................................... 7,668
Temporary difference carrying from restructuring........ 1,886
Reserve for employees’ retirement allowance ............. 3,036
Inventories, etc. ........................................................... 3,827
Other, net...................................................................... 5,704
Subtotal .................................................................... 34,935
Valuation allowance.......................................................... (6,413)
Deferred tax assets total .......................................... 28,522
Gross deferred tax liabilities.............................................
Deferral of taxes on profit of fixed assets......................... (1,798)
Net deferred tax assets .................................................... ¥26,724
8. Shareholders’ Equity
The Japanese Commercial Code provides that an amount equivalent
to at least 10 per cent of cash distributions (cash dividends and
bonuses to directors and corporate auditors) paid in a fiscal period
)