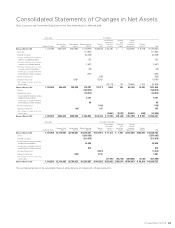
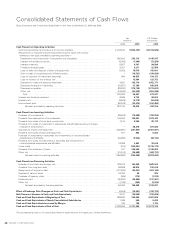
Sharp 2009 Annual Report Download - page 51
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 51 of the 2009 Sharp annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
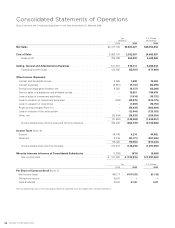
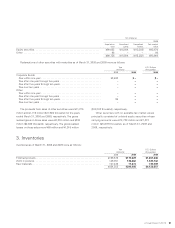
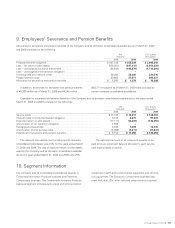
Research and development expenses are charged to income
as incurred. The research and development expenses are
charged to income amounted to ¥196,186 million and
¥195,525 million ($2,015,722 thousand) for the years ended
March 31, 2008 and 2009, respectively.
Software costs are recorded principally in other assets.
Software used by the Company is amortized using the
straight-line method over the estimated useful life of princi-
pally 5 years, and software embedded in products is amor-
tized over the forecasted sales quantity.
The Company and some of its consolidated subsidiaries use
derivative financial instruments, including foreign exchange
forward contracts and interest rate swap agreements, in
order to hedge the risk of fluctuations in foreign currency
exchange rates and interest rates associated with assets and
liabilities denominated in foreign currencies, investments in
securities and debt obligations.
All derivative financial instruments are stated at fair value
and recorded on the balance sheets. The deferred method is
used for recognizing gains or losses on hedging instruments
and the hedged items. When foreign exchange forward con-
tracts meet certain conditions, the hedged items are stated
by the forward exchange contract rates.
If certain hedging criteria are met, interest rate swaps are
not recognized at their fair values as an alternative method under
Japanese accounting standards. The net amounts received or
paid for such interest rate swap arrangements are charged or
credited to income as incurred.
Derivative financial instruments are used based on inter-
nal policies and procedures on risk control.
The risks of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange
rates and interest rates have been assumed to be completely
hedged over the period of hedging contracts as the major
conditions of the hedging instruments and the hedged items
are consistent. Accordingly, an evaluation of the effectiveness
of the hedging contracts is not required.
The credit risk of such derivatives is assessed as being
low because the counter-parties of these transactions have
good credit ratings with financial institutions.
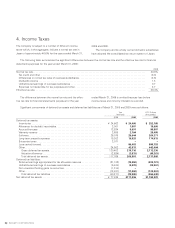
(1) Depreciation Methods Used for Amortization for
Tangible Fixed Assets
Effective for the year ended March 31, 2008, pursuant to an
amendment to the Corporate Tax Law, the Company and its
domestic consolidated subsidiaries have depreciated tangible
fixed assets acquired on and after April 1, 2007 in accordance
with the method stipulated in the amended Corporate Tax Law.
As a result, for the year ended March 31, 2008, operating
income and income before income taxes and minority interests
decreased by ¥7,234 million, compared to amounts calculated
under the previous method. The effect of this change on seg-
mented information is stated in Note 10. Segment Information.
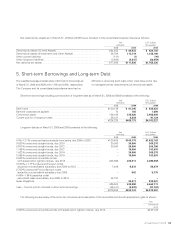
(2) Accounting Method for Reserve for Director and
Corporate Auditor Retirement Benefits
Effective for the year ended March 31, 2008, the amended
“Auditing Treatment Relating to Reserve Defined under the
Special Tax Measurement Law, Reserve Defined under the
Special Law and Reserve for Director and Corporate Auditor
Retirement Benefits” (The Japanese Institute of Certified
Public Accountants (“JICPA”) Auditing and Assurance Prac-
tice Committee Report No. 42, April 13, 2007) have been
adopted. As a result, for the year ended March 31, 2008,
operating income and income before income taxes and
minority interests decreased by ¥133 million and ¥896 million,
respectively, compared to amounts calculated under the
previous method. The effect of this change on segmented
information is stated in Note 10. Segment Information.
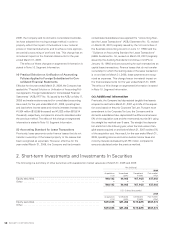
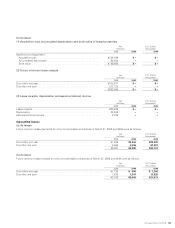
(3) Standard and Method for Measurement
of Inventories
Effective for the year ended March 31, 2009, the Company and
its domestic consolidated subsidiaries have applied the
“Accounting Standard for Measurement of Inventories”
(Accounting Standards Board of Japan (ASBJ) Statement No.
9, issued by the ASBJ on July 5, 2006). As a result, for the year
ended March 31, 2009, operating loss and loss before income
taxes and minority interests increase by ¥5,274 million
($54,371 thousand) and ¥12,919 million ($133,186 thousand),
respectively, compared to amounts calculated under the previ-
ous method.
Also, valuation methods for raw materials and work in
process had previously been based on the last invoice
method. However, effective for the year ended March 31,