Telus 2007 Annual Report Download - page 32
Download and view the complete annual report
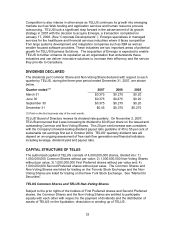
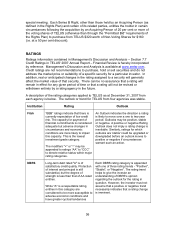
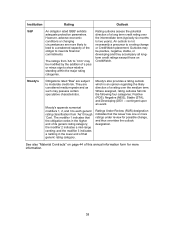
Please find page 32 of the 2007 Telus annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report. 32
agreement to be acquired by a group of private equity investors. The sale of BCE is
expected to be completed in the first half of 2008. It is anticipated that there will be a
significant change in BCE’s operational and investment priorities after the completion of
the privatization. It is also expected that BCE will reduce its public disclosure going
forward.
Wireless segment
TELUS offers wireless voice and data services to consumers and businesses nationally
on both the ESMR (branded Mike) and the PCS/cellular networks and competes in both
the prepaid and postpaid markets.
The primary competitors with TELUS are Bell Mobility and Rogers Wireless, both of
which have national networks, a broad offering of wireless voice and data services for
consumers and businesses, and a large existing customer base. In April 2005, Virgin
Mobile began offering services across Canada. Virgin Mobile is a Mobile Virtual Network
Operator (“MVNO”) which is owned in part by Bell Mobility and utilizes the Bell Mobility
network for the provisioning of services. In addition, both Bell Mobility and Rogers
Communications are supporting other MVNO partnerships with cable-TV companies
such as Videotron and Eastlink, and other resellers, such as President’s Choice, Petro-
Canada and 7-Eleven. In the price-sensitive market, Bell and Rogers are promoting
their respective discount brand offerings to compete against the MVNOs and TELUS.
Competition within the wireless market is anticipated to remain intense. There is a high
probability that the auction processes for AWS or a future auction of 2.5 GHz spectrum
will lead to the entry of additional wireless providers on a regional and/or national basis
as early as 2009. These new competitors are expected to benefit from subsidized
spectrum, mandated roaming and tower sharing rights which will afford the advantage of
lower cost of entry than would otherwise be the case.
TELUS also competes with numerous national, regional and local-paging companies for
paging customers in Alberta, B.C., and eastern Québec. TELUS offers a number of
wireless Internet offerings using the networks noted above as well as wireless LAN
services such as WiFi (802.11) in so-called “hotspots” and other areas utilizing
unlicenced spectrum. In offering wireless Internet and LAN access service, TELUS
competes, to a limited extent, with wireline business Internet access providers. It also
competes with major equipment manufacturers for private radio engineered systems.
Other emerging competitive services
Over the longer term there are a number of factors that are expected to increase
competition in the communications industry. Of note is the competitive escalation
resulting from the continuing convergence of cable-TV, satellite, computer, wireline and
wireless technologies. In November 2005, TELUS commercially launched TELUS TV
within select neighbourhoods in the Edmonton and Calgary markets. In 2006, the
expansion continued with a targeted commercial launch in Vancouver and in 2007
TELUS TV was launched in Rimouski. There are plans underway to launch TELUS TV
in other major centres within its ILEC territories. In this segment, TELUS competes with
established cable-TV video providers, such as Shaw Communications and Cogeco, and
with direct-to-home broadcast satellite companies, such as Bell ExpressVu and Star
Choice.