Progressive 2013 Annual Report Download - page 7
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 7 of the 2013 Progressive annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
upon their expected auction date (generally 7-49 days) rather than on their contractual maturity date (which is greater than one
year at original issuance). In the event that an auction fails, the security may need to be reclassified from short-term. Changes in
fair value of these securities, net of deferred income taxes, are reflected as unrealized gains (losses) in accumulated other
comprehensive income.
Trading securities are securities bought principally for the purpose of sale in the near term. To the extent we have trading
securities, changes in fair value would be recognized in income in the current period. Derivative instruments, which may be
used for trading purposes or classified as trading derivatives due to the characteristics of the transaction, are discussed
below.
Derivative instruments may include futures, options, forward positions, foreign currency forwards, interest rate swap
agreements, and credit default swaps and may be used in the portfolio for general investment purposes or to hedge the
exposure to:
• Changes in fair value of an asset or liability (fair value hedge)
• Foreign currency of an investment in a foreign operation (foreign currency hedge), or
• Variable cash flows of a forecasted transaction (cash flow hedge).
To the extent we have derivatives held for general investment purposes, these derivative instruments are recognized as
either assets or liabilities and measured at fair value, with changes in fair value recognized in income as a component of net
realized gains (losses) on securities during the period of change.
Derivatives designated as hedges are required to be evaluated on established criteria to determine the effectiveness of their
correlation to, and ability to reduce the designated risk of, specific securities or transactions. Effectiveness is required to be
reassessed regularly. Hedges that are deemed to be effective would be accounted for as follows:
•Fair value hedge: changes in fair value of the hedge, as well as the hedged item, would be recognized in income
in the period of change while the hedge is in effect.
•Foreign currency hedge: changes in fair value of the hedge, as well as the hedged item, would be reflected as a
change in translation adjustment as part of accumulated other comprehensive income. Gains and losses on the
foreign currency hedge would offset the foreign exchange gains and losses on the foreign investment as they are
recognized into income.
•Cash flow hedge: changes in fair value of the hedge would be reported as a component of accumulated other
comprehensive income and subsequently amortized into earnings over the life of the hedged transaction.
If a hedge is deemed to become ineffective or discontinued, the following accounting treatment would be applied:
•Fair value hedge: the derivative instrument would continue to be adjusted through income, while the adjustment in
the change in value of the hedged item would be reflected as a change in unrealized gains (losses) as part of
accumulated other comprehensive income.
•Foreign currency hedge: changes in the value of the hedged item would continue to be reflected as a change in
translation adjustment as part of accumulated other comprehensive income, but the derivative instrument would be
adjusted through income for the current period.
•Cash flow hedge: changes in fair value of the derivative instrument would be reported in income for the current
period.
For all derivative positions, net cash requirements are limited to changes in fair values, which may vary based upon
changes in interest rates, currency exchange rates, and other factors. Exposure to credit risk is limited to the carrying value;
collateral may be required to limit credit risk. We have elected not to offset fair value amounts that arise from derivative
positions with the same counterparty under a master netting arrangement.
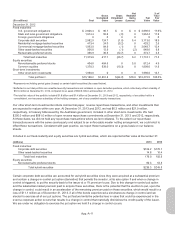
Investment securities are exposed to various risks such as interest rate, market, credit, and liquidity risk. Fair values of
securities fluctuate based on the nature and magnitude of changing market conditions; significant changes in market
conditions could materially affect the portfolio’s value in the near term. We regularly monitor our portfolio for price changes,
which might indicate potential impairments, and perform detailed reviews of securities with unrealized losses. In such cases,
changes in fair value are evaluated to determine the extent to which such changes are attributable to: (i) fundamental
factors specific to the issuer, such as financial condition, business prospects, or other factors, (ii) market-related factors,
such as interest rates or equity market declines, or (iii) credit-related losses, where the present value of cash flows expected
to be collected are lower than the amortized cost basis of the security.
App.-A-7