Intel 2010 Annual Report Download - page 95
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 95 of the 2010 Intel annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
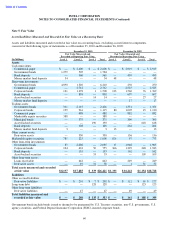
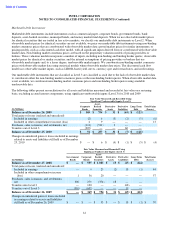
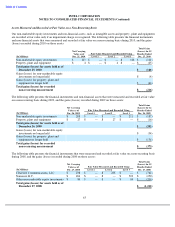
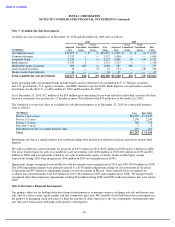
INTEL CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
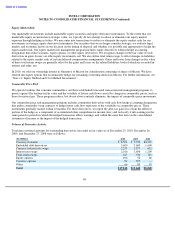
Currency Exchange Rate Risk
We are exposed to currency exchange rate risk and generally hedge our exposures with currency forward contracts, currency
options, or currency interest rate swaps. Substantially all of our revenue and a majority of our expense and capital purchasing
activities are transacted in U.S. dollars. However, certain operating expenditures and capital purchases are incurred in or
exposed to other currencies, primarily the Japanese yen, the euro, and the Israeli shekel. We have established balance sheet
and forecasted transaction currency risk management programs to protect against fluctuations in fair value and the volatility of
future cash flows caused by changes in exchange rates. Our non-U.S.-dollar-denominated investments in debt instruments and
loans receivable are generally hedged with offsetting currency forward contracts or currency interest rate swaps. These
programs reduce, but do not entirely eliminate, the impact of currency exchange movements.
Our currency risk management programs include:
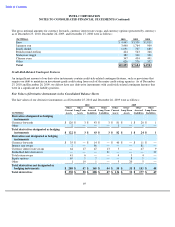
Interest Rate Risk
Our primary objective for holding investments in debt instruments is to preserve principal while maximizing yields. We
generally swap the returns on our investments in fixed-rate debt instruments with remaining maturities longer than six months
into U.S.-dollar three-month LIBOR-based returns, unless management specifically approves otherwise. These swaps are
settled at various interest payment times involving cash payments at each interest and principal payment date, with the
majority of the contracts having quarterly payments.
Our interest rate risk management programs include:
67
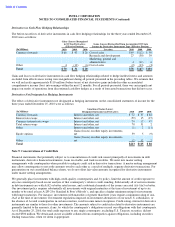
• Currency derivatives with cash flow hedge accounting designation
that utilize currency forward contracts and currency
options to hedge exposures to the variability in the U.S.-dollar equivalent of anticipated
non-U.S.-dollar-denominated cash flows. These instruments generally mature within 12 months. All of our currency
forward contracts are settled at maturity involving one cash-payment exchange. For these derivatives, we report the
after-tax gain or loss from the effective portion of the hedge as a component of accumulated other comprehensive
income (loss) and reclassify it into earnings in the same period or periods in which the hedged transaction affects
earnings, and within the same line item on the consolidated statements of income as the impact of the hedged
transaction.
• Currency derivatives without hedge accounting designation that utilize currency forward contracts or currency interest
rate swaps to economically hedge the functional currency equivalent cash flows of recognized monetary assets and
liabilities and non-U.S.-dollar-denominated debt instruments classified as trading assets. The maturity of these
instruments generally occurs within 12 months, except for derivatives associated with certain long-term equity-related
investments and our loans receivable that generally mature within five years. The currency interest rate swaps are
settled at various interest payment times involving cash payments at each interest and principal payment date, with the
majority of the contracts having quarterly payments. Changes in the U.S.-dollar-equivalent cash flows of the
underlying assets and liabilities are approximately offset by the changes in fair values of the related derivatives. We
record net gains or losses in the line item on the consolidated statements of income most closely associated with the
economic underlying, primarily in interest and other, net, except for equity-related gains or losses, which we primarily
record in gains (losses) on other equity investments, net.
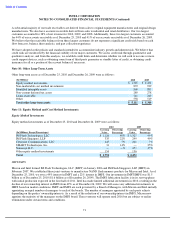
•
Interest rate derivatives with cash flow hedge accounting designation
that utilize interest rate swap agreements to
modify the interest characteristics of debt instruments. For these derivatives, we report the after-tax gain or loss from
the effective portion of the hedge as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) and reclassify it
into earnings in the same period or periods in which the hedged transaction affects earnings, and within the same line
item on the consolidated statements of income as the impact of the hedged transaction.
•
Interest rate derivatives without hedge accounting designation
that utilize interest rate swaps and currency interest rate
swaps in economic hedging transactions, including hedges of non-U.S.-dollar-denominated debt instruments classified
as trading assets. Floating interest rates on the swaps are reset on a monthly, quarterly, or semiannual basis. Changes in
fair value of the debt instruments classified as trading assets are generally offset by changes in fair value of the related
derivatives, both of which are recorded in interest and other, net.