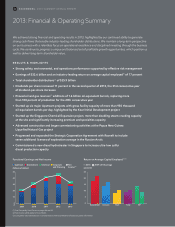
Exxon 2013 Annual Report Download - page 9
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 9 of the 2013 Exxon annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
HIGH-IMPACT TECHNOLOGIES
Advances in technology have enabled the industry to produce more oil and gas, while reducing the environmental
impact of energy production. Technologies are being utilized to enable production from difficult environments,
like arctic and deepwater, and to “unlock” oil and gas production from tight rock formations.
For example, the Arctic is the world’s largest frontier for undiscovered resources in one of the most challenging
operating environments. With its remote location, harsh weather, and dynamic ice cover, new technology solutions
range from the use of extended-reach drilling, ice-resistant platforms, iceberg surveillance research, and
computerized models to simulate and predict ice impacts.
Deepwater oil and gas production (more than 1,300 feet of water) is expected to grow by more than 150 percent
from 2010 to 2040 and will represent more than 12 percent of global supplies. The growth is dramatic considering
that deepwater production was nearly nonexistent several decades ago.
New drilling and completion technologies also have enabled the recent growth in production from shale and
other unconventional oil and gas reservoirs in North America. These reservoirs are produced using a combination
of hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling. Unconventional drilling activity also leads to growth in natural gas
liquids, another important contribution to the growth in global liquids supply.
PHOTO: The Arkutun-Dagi gravity-based structure (GBS) is located approximately 15 miles east of Sakhalin Island,
Russia. The platform topsides, with drilling and production equipment, will be installed on the GBS. The project has
a peak gross production capacity of 90 thousand barrels per day and is scheduled to start up in 2014.
7