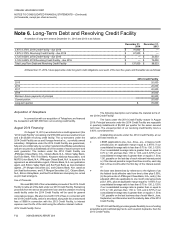
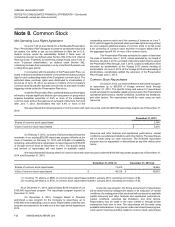
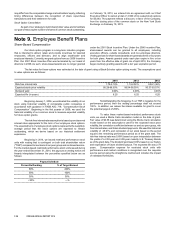
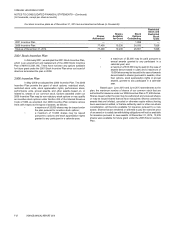
Vonage 2014 Annual Report Download - page 87
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 87 of the 2014 Vonage annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
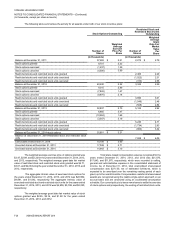
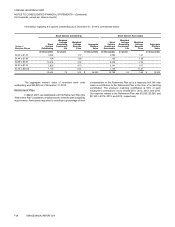
VONAGE HOLDINGS CORP.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
(In thousands, except per share amounts)
F-32 VONAGE ANNUAL REPORT 2014
settlement of all outstanding patent disputes, including the California
action and the ITC complaint. The parties have agreed to dismiss all
patent cases between themselves and their downstream customers
(including Vonage) worldwide, granting to each other licenses under
their respective patents.
Commercial Litigation
Merkin & Smith, et als. On September 27, 2013, Arthur Merkin
and James Smith filed a putative class action lawsuit against Vonage
America, Inc. in the Superior Court of the State of California, County of
Los Angeles, alleging that Vonage violated California’s Unfair
Competition Law by charging its customers fictitious 911 taxes and fees.
On October 30, 2013, Vonage filed a notice removing the case to the
United States District Court for the Central District of California. On
October 30, 2013 the case was assigned to a United States District
Judge and a Magistrate Judge. On November 26, 2013, Vonage filed
its Answer to the Complaint. On December 4, 2013, Vonage filed a
Motion to Compel Arbitration. On February 4, 2014, the Court denied
Vonage’s Motion to Compel Arbitration. On March 5, 2014, Vonage filed
an appeal with the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit
of the decision denying Vonage’s Motion to Compel Arbitration. On
March 6, 2014, Vonage moved to stay the district court proceedings
pending its appeal; the Court granted Vonage’s stay motion on March
26, 2014. Briefing on the appeal is now complete, though oral argument
has not yet been scheduled.
Regulation
Telephony services are subject to a broad spectrum of state
and federal regulations. Because of the uncertainty over whether Voice
over Internet Protocol (“VoIP”) should be treated as a
telecommunications or information service, we have been involved in a
substantial amount of state and federal regulatory activity.
Implementation and interpretation of the existing laws and regulations
is ongoing and is subject to litigation by various federal and state
agencies and courts. Due to the uncertainty over the regulatory
classification of VoIP service, there can be no assurance that we will
not be subject to new regulations or existing regulations under new
interpretations, and that such change would not introduce material
additional costs to our business.
Federal - Net Neutrality
Clear and enforceable net neutrality rules would make it more
difficult for broadband Internet service providers to block or discriminate
against Vonage service. Also explicitly applying net neutrality rules to
wireless broadband Internet service could create greater opportunities
for VoIP applications that run on wireless broadband Internet service.
In October 2009, the FCC proposed the adoption of enforceable net
neutrality rules for both wired and wireless broadband Internet service
providers. The proposed rules would prohibit wired and wireless
broadband Internet service providers from blocking or hindering lawful
content, applications, or services and from unreasonably discriminating
when transmitting lawful network traffic. In addition, broadband Internet
service providers would have to publicly disclose certain information
about their network management practices. In December 2010, the FCC
adopted enforceable net neutrality rules based on its October 2009
proposal. All of the proposed rules in the October 2009 proposal applied
to wired broadband Internet providers. The FCC applied some but not
all of the proposed rules to wireless broadband service. Wireless
broadband Internet services providers are prohibited from blocking or
hindering voice or video applications that compete with the broadband
Internet service provider's voice or video services. Wireless providers
are also subject to transparency requirements, but they are not subject
to the prohibition on unreasonable discrimination that applies to wired
broadband Internet services providers. Final rules were filed in the
Federal Register in September 2011. Shortly thereafter, a number of
parties filed appeals of the rules in various federal circuit courts; some
alleging that the FCC lacks authority to apply net neutrality rules to
broadband service providers and some alleging that the rules did not
go far enough. The D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals was selected by lottery
to decide the appeals and the appeals alleging that the rules did not go
far enough were dropped. The D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals heard oral
arguments on the appeal on September 9, 2013. On January 14, 2014,
the D.C. Circuit vacated the anti-blocking and the unreasonable
discrimination provisions of the rules. A vote on the new net neutrality
rules currently is expected at the February 26, 2015 FCC meeting.
Federal - Intercarrier Compensation
On February 9, 2011, the FCC released a Notice of Proposed
Rulemaking on reforming universal service and the intercarrier
compensation (“ICC”) system that governs payments between
telecommunications carriers primarily for terminating traffic. In particular,
the FCC indicated that it has never determined the ICC obligations for
VoIP service and sought comment on a number of proposals for how
VoIP should be treated in the ICC system. The FCC's adoption of an
ICC proposal will impact Vonage's costs for telecommunications
services. On October 27, 2011, the FCC adopted an order reforming
universal service and ICC. The FCC order provides that VoIP originated
calls will be subject to interstate access charges for long distance calls
and reciprocal compensation for local calls that terminate to the public
switched telephone network (“PSTN”). It also subjected PSTN originated
traffic directed to VoIP subscribers to similar ICC obligations. The
termination charges for all traffic, including VoIP originated traffic, will
transition over several years to a bill and keep arrangement (i.e., no
termination charges). Numerous parties filed appeals of the FCC order
in multiple federal circuit courts of appeal. The 10th Circuit Court of
Appeals was selected by lottery to decide the appeals. The appeals are
pending.
Federal - Universal Service Contribution Reform
On April 30, 2012, the FCC released a Further Notice of
Proposed Rulemaking on reforming federal universal service fund
(“USF”) contributions. Currently USF contributions are assessed on the
interstate and international revenue of traditional telephone carriers and
interconnected VoIP providers like Vonage. The level of USF
assessments on these providers has been going up over time because
of decreases in the revenue subject to assessment due to substitution
of non-assessable services such as non-interconnected VoIP services.
If the FCC does reform USF contributions, it is likely that Vonage's
contribution burden will decline.
Federal - E-Rate Reform
On December 19, 2013, the FCC released a Second Report and
Order and Order on Reconsideration modernizing the E-Rate program.
The E-Rate program subsidizes voice and data services for schools and
libraries and is one component of the federal universal service fund.
The December 19 order increased the size of the E-Rate fund to $3.9B
in available annual funding. This represents an approximately $1.5B
annual (17%) increase in the overall size of the universal service fund.
This increase in the size of the fund will likely lead to increased USF
contribution levels for Vonage services subject to assessment for federal
USF.
Federal - Rural Call Completion Issues
On February 7, 2013, the FCC released a Notice of Proposed
Rulemaking on rural call completion issues. The Notice of Proposed
Rulemaking (NPRM) proposed new detailed reporting requirements to
gauge rural call completion performance. Rural carriers have argued
that VoIP provider call completion performance to rural areas is generally
poor. On October 28, 2013, the FCC adopted an order on rural call
completion that imposes new reporting obligations and restricts certain
call signaling practices. The call signaling rules went into effect on
January 31, 2014. We filed for extensions that the FCC granted on