Red Lobster 1999 Annual Report Download - page 11
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 11 of the 1999 Red Lobster annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes
to Consolidated Financial Statements
32
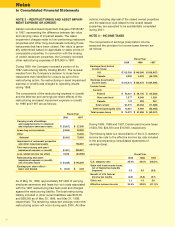
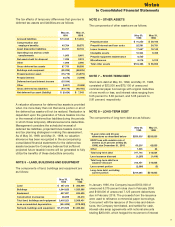
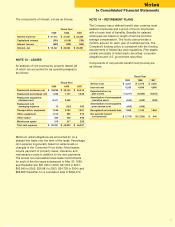
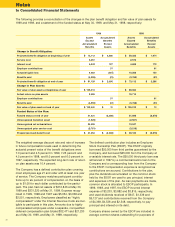
I. Income Taxes
The Company provides for federal and state income
taxes currently payable, as well as for those deferred
because of temporary differences between reporting
income and expenses for financial statement purposes
and income and expenses for tax purposes. Federal
income tax credits are recorded as a reduction of income
taxes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized
for the future tax consequences attributable to differ-
ences between the financial statement carrying amounts
of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax
bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured
using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable
income in the years in which those temporary differences
are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on
deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates
is recognized in income in the period that includes the
enactment date.
J. Statements of Cash Flows
For purposes of the consolidated statements of cash
flows, amounts receivable from credit card companies
and investments purchased with a maturity of three
months or less are considered cash equivalents.
K. Net Earnings (Loss) Per Share
In February 1997, the Financial Accounting Standards
Board issued Statement of Financial Accounting
Standards No. 128 (SFAS 128), “Earnings Per Share,”
which requires presentation of basic and diluted earnings
per share. Basic earnings per share is computed by
dividing income available to common shareholders by
the weighted-average number of common shares
outstanding for the reporting period. Diluted earnings per
share reflects the potential dilution that could occur if
securities or other contracts to issue common stock
were exercised or converted into common stock. As
required, the Company adopted the provisions of
SFAS 128 during 1998. All prior year weighted-average
and per share information has been restated in accor-
dance with SFAS 128. Outstanding stock options issued
by the Company represent the only dilutive effect reflected
in diluted weighted-average shares.
Options to purchase 120,200 and 868,300 shares
of common stock were excluded from the calculation
of diluted earnings per share for the years ended
May 30, 1999, and May 31, 1998, respectively, because
their exercise prices exceeded the average market price
of common shares for the period. All options were
excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per
share for the year ended May 25, 1997, because their
inclusion would have been anti-dilutive.
L. Derivative Financial and Commodity Instruments
On January 31, 1997, the Securities and Exchange
Commission (SEC) issued amended disclosure rules for
derivatives and exposures to market risk from derivative
and other financial and certain commodity instruments.
Enhanced accounting policy disclosures in accordance
with this SEC release follow.
The Company may, from time to time, use financial and
commodities derivatives in the management of interest
rate and commodities pricing risks that are inherent in
its business operations. The Company may also use
financial derivatives as part of its stock repurchase
program as described in Note 10. Such instruments are
not held or issued for trading or speculative purposes.
The Company may, from time to time, use interest-rate
swap and cap agreements in the management of interest
rate exposure. The interest rate differential to be paid or
received is normally accrued as interest rates change,
and is recognized as a component of interest expense
over the life of the agreements. If an agreement is termi-
nated prior to the maturity date and is characterized as a
hedge, any accrued rate differential would be deferred
and recognized as interest expense over the life of the
hedged item. The Company uses commodities hedging
instruments, including forwards, futures and options, to
reduce the risk of price fluctuations related to future raw
materials requirements for commodities such as coffee,
soybean oil and shrimp. The terms of such instruments
generally do not exceed 12 months, and depend on the
commodity and other market factors. Deferred gains and
losses are subsequently recorded as cost of products
sold in the statements of earnings (loss) when the
inventory is sold. If the inventory is not acquired and
the hedge is disposed of, the deferred gain or loss is
recognized immediately in cost of products sold. The
Company believes that it does not have material risk
from any of the above financial instruments, and the
Company does not anticipate any material losses from
the use of such instruments.
M. Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity
with generally accepted accounting principles requires
management to make estimates and assumptions that
affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and
disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date
of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of
revenues and expenses during the reporting period.
Actual results could differ from those estimates.