Intel 2003 Annual Report Download - page 61
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 61 of the 2003 Intel annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
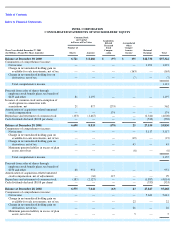
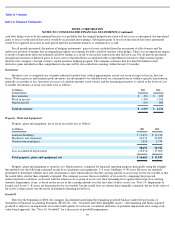
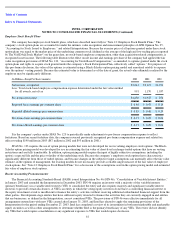
INTEL CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1: Basis of Presentation
Intel Corporation has a fiscal year that ends on the last Saturday in December. Fiscal year 2003, a 52-week year, ended on December 27,
2003. Fiscal year 2002 was a 52-week year that ended on December 28, and fiscal year 2001, also a 52-
week year, ended on December 29. The
next 53-week year will end on December 31, 2005.
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Intel and its wholly owned subsidiaries. Intercompany accounts and
transactions have been eliminated. Partially owned, non-controlled equity affiliates are accounted for under the equity method. Accounts
denominated in non-U.S. currencies have been remeasured using the U.S. dollar as the functional currency. Certain amounts reported in
previous years have been reclassified to conform to the 2003 presentation.
Note 2: Accounting Policies
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. requires management to
make estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes. The accounting estimates
that require management’s most difficult and subjective judgments include the assessment of recoverability of property, plant, and equipment
and goodwill; the valuation of non-marketable equity securities and inventory; and the recognition and measurement of income tax assets and
liabilities. The actual results experienced by the company may differ from management’s estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Highly liquid debt securities with insignificant interest rate risk and with original maturities from the date of purchase of three months or
less are classified as cash and cash equivalents.
Investments
Trading Assets. Trading assets are stated at fair value, with gains or losses resulting from changes in fair value recognized currently in
earnings. The company elects to classify as trading assets a portion of its marketable debt securities. For these debt securities, gains or losses
from changes in fair value due to interest rate and currency market fluctuations, offset by losses or gains on related derivatives, are included in
interest and other, net. A portion of the company’s marketable equity securities may from time to time be classified as trading assets, if the
company no longer deems the investments to be strategic in nature at the time of trading asset designation, and has the ability and intent to
mitigate equity market risk through sale or the use of derivative instruments. For these marketable equity securities, gains or losses from
changes in fair value, primarily offset by losses or gains on related derivative instruments, are included in gains (losses) on equity securities,
net. Also included in trading assets is a marketable equity portfolio held to generate returns that seek to offset changes in liabilities related to
the equity market risk of certain deferred compensation arrangements. Gains or losses from changes in fair value of these equity securities,
offset by losses or gains on the related liabilities, are included in interest and other, net. The company also uses fixed income investments and
derivative instruments to seek to offset the remaining portion of the changes in the compensation liabilities.
Available-for-Sale Investments. Investments designated as available-for-sale include marketable debt and equity securities. Investments
that are designated as available-for-sale as of the balance sheet date are reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses, net of tax,
recorded in stockholders’
equity. The cost of securities sold is based on the specific identification method. Realized gains and losses on the sale
of debt securities are recorded in interest and other, net. Realized gains or losses on the sale or exchange of equity securities and declines in
value judged to be other than temporary are recorded in gains (losses) on equity securities, net. Marketable equity securities are presumed to be
impaired if the fair value is less than the cost basis continuously for six months, absent compelling evidence to the contrary.
Debt securities with original maturities greater than three months and remaining maturities less than one year are classified as short-term
investments. Debt securities with remaining maturities greater than one year are classified as long-term investments.
The company acquires certain equity investments for the promotion of business and strategic objectives, and to the extent that these
investments continue to have strategic value, the company typically does not attempt to reduce or eliminate the inherent market risks through
hedging activities. The marketable portion of these investments is included in marketable strategic equity securities.
56