Bridgestone 2004 Annual Report Download - page 12
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 12 of the 2004 Bridgestone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
10
Bridgestone Annual Report 2004
In 2004, we agreed to purchase a rubber estate in Sumatra, Indonesia, from Goodyear Tire &
Rubber Company. That will give us our second rubber estate in Indonesia, where we also cultivate
rubber trees in Kalimantan. The Bridgestone Group has a rubber estate in Liberia, too. Group com-
panies process natural rubber at the estates and at plants in Thailand and in China.
The rubber estates are invaluable as platforms for research and development. Researchers at our
rubber estates in Indonesia study plant cultivation with an eye to increasing yields and to securing
higher grades of rubber. They also conduct research on ways of raising quality and productivity in
rubber processing. Working in close coordination with our field researchers are the materials engi-
neering specialists at our technical center in Tokyo.
Bridgestone Group companies produce carbon black in Japan and in Thailand. They also work
closely with the materials engineering team at our technical center in Tokyo. Advances in carbon
black, such as the development of long-chain carbon, have figured prominently in Bridgestone
product breakthroughs. Our self-sufficiency rate is extremely high in carbon black for some special
applications in tires.
The Bridgestone Group manufactures synthetic rubber at two U.S. plants and conducts research
and development on that material in Akron, Ohio. The company-owned plants are an important
source of synthetic rubber for Bridgestone Group operations in the Americas.
Steel cord is yet another material sector where hands-on participation in R&D and in production
reinforces our technological capabilities in tires. Bridgestone Group companies produce steel cord
at plants in Japan, the United States, Italy, and Thailand. A Bridgestone plant under construction
Bridgestone is the only tire manufacturer that has in-house supply capabilities in natural
rubber, synthetic rubber, carbon black, and steel cord. Our investment in expanded raw mate-
rial production will total about ¥40 billion over the five years to 2007. We recently opened a
carbon black plant in Thailand, and Bridgestone Group companies are expanding raw material
production capacity in Japan, in the United States, and in Asian nations other than Japan.
Global network
While continuing to purchase
most of our raw materials from
third-party suppliers, we will
upgrade our in-house capabili-
ties in developing, producing,
and using those materials. That
will help us create better tires,
and it will help ensure reliable
access to crucial raw materials.
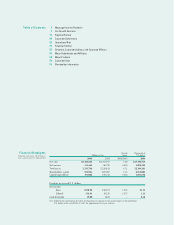
Our Growth Scenario
Raw Materials