3M 2005 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2005 3M annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
56
In December 2005, the Company’s $350 million of dealer remarketable securities were remarketed for one year.
They were reissued with a fixed coupon rate of 5.65%. These securities, which are classified as current portion of
long-term debt, were issued in December 2000. The remarketable securities can be remarketed annually, at the
option of the dealer, for a year each time, with a final maturity date of December 2010.
NOTE 9. Derivatives and Other Financial Instruments
The Company uses interest rate swaps, currency swaps, and forward and option contracts to manage risks generally
associated with foreign exchange rate, interest rate and commodity market volatility. The information that follows
explains the various types of derivatives and financial instruments, and includes a table that recaps cash flow hedging
amounts.
Foreign Currency Forward and Option Contracts: The Company enters into foreign exchange forward contracts,
options and swaps to hedge against the effect of exchange rate fluctuations on cash flows denominated in foreign
currencies and certain intercompany financing transactions. These transactions are designated as cash flow hedges.
At December 31, 2005, the Company had various open foreign exchange forward and option contracts, the majority
of which had maturities of one year or less. The amounts at risk are not material because the Company has the ability
to generate offsetting foreign currency cash flows. The settlement or extension of these derivatives will result in
reclassifications to earnings in the period during which the hedged transactions affect earnings (from other
comprehensive income). The maximum length of time over which 3M is hedging its exposure to the variability in future
cash flows for a majority of the forecasted transactions, excluding those forecasted transactions related to the
payment of variable interest on existing financial instruments, is 12 months. Based on exchange rates at December
31, 2005, the Company expects to reclassify to earnings over the next 12 months a majority of the cash flow hedging
instruments after-tax gain of $38 million (with the impact largely offset by foreign currency cash flows from underlying
hedged items). Hedge ineffectiveness was not material for the years 2005, 2004 and 2003. Amounts recorded in
accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to cash flow hedging instruments follow.
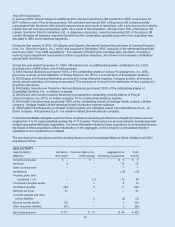
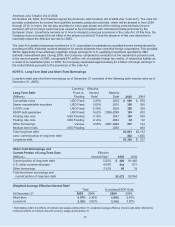
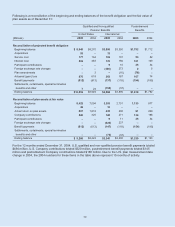
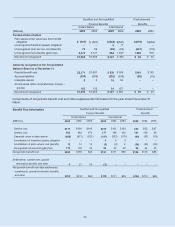
Cash Flow Hedging Instruments Twelve months ended
Net of Tax December 31
(Millions) 2005 2004 2003
Beginning balance $ (42) $ (45) $ (39)
Changes in fair value of derivatives 70 (48) (102)
Net losses reclassified into earnings from equiity 10 51 96
Total activity 80 3 (6)
Ending balance $ 38 $ (42) $ (45)
Interest Rate and Currency Swaps: The Company manages interest expense using a mix of fixed and floating rate
debt. To help manage borrowing costs, the Company may enter into interest rate swaps. Under these arrangements,
the Company agrees to exchange, at specified intervals, the difference between fixed and floating interest amounts
calculated by reference to an agreed-upon notional principal amount. The Company uses interest rate and currency
swaps to manage interest rate risk related to borrowings.
At December 31, 2005, the Company did not have any interest rate swaps designated as fair value hedges of
underlying fixed rate obligations. The fair value of swaps at December 31, 2004 was $3 million. The mark-to-market of
these fair value hedges is recorded as gains or losses in interest expense and is offset by the gain or loss on the
underlying debt instrument, which also is recorded in interest expense. These fair value hedges are 100% effective
and, thus, there is no impact on earnings due to hedge ineffectiveness.
As circumstances warrant, the Company also uses cross-currency interest rate swaps to hedge foreign currency and
interest rates. As part of this strategy, in September 2003, the Company entered into a three-year combined interest
rate and currency swap with a notional amount of $300 million. This transaction is a partial hedge of 3M’s net
investment in 3M’s Japanese subsidiaries. This swap converts a variable rate U.S. dollar exposure to a variable rate
yen-denominated exposure.