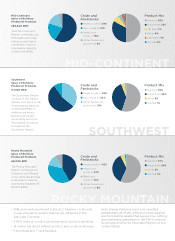
HollyFrontier 2015 Annual Report Download - page 12
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 12 of the 2015 HollyFrontier annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Content
4
DEFINITIONS
Within this report, the following terms have these specific meanings:
“Alkylation” means the reaction of propylene or butylene (olefins) with isobutane to form an iso-paraffinic gasoline (inverse
of cracking).
“Aromatic oil” is long chain oil that is highly aromatic in nature and is used to manufacture tires and industrial rubber
products and in the production of specialty asphalt.
“BPD” means the number of barrels per calendar day of crude oil or petroleum products.
“BPSD” means the number of barrels per stream day (barrels of capacity in a 24 hour period) of crude oil or petroleum
products.
“Biodiesel” means an alternative fuel produced from renewable biological resources.
“Black wax crude oil” is a low sulfur, low gravity crude oil produced in the Uintah Basin in Eastern Utah that has certain
characteristics that require specific facilities to transport, store and refine into transportation fuels.
“Catalytic reforming” means a refinery process which uses a precious metal (such as platinum) based catalyst to convert
low octane naphtha to high octane gasoline blendstock and hydrogen. The hydrogen produced from the reforming process is used
to desulfurize other refinery oils and is a primary source of hydrogen for the refinery.
“Cracking” means the process of breaking down larger, heavier and more complex hydrocarbon molecules into simpler
and lighter molecules.
“Crude oil distillation” means the process of distilling vapor from liquid crudes, usually by heating, and condensing the
vapor slightly above atmospheric pressure turning it back to liquid in order to purify, fractionate or form the desired products.
“Ethanol” means a high octane gasoline blend stock that is used to make various grades of gasoline.
“FCC,” or fluid catalytic cracking, means a refinery process that breaks down large complex hydrocarbon molecules into
smaller more useful ones using a circulating bed of catalyst at relatively high temperatures.
“Hydrodesulfurization” means to remove sulfur and nitrogen compounds from oil or gas in the presence of hydrogen and
a catalyst at relatively high temperatures.
“Hydrogen plant” means a refinery unit that converts natural gas and steam to high purity hydrogen, which is then used in
the hydrodesulfurization, hydrocracking and isomerization processes.
“HF alkylation” or hydrofluoric alkylation, means a refinery process which combines isobutane and C3/C4 olefins using
HF acid as a catalyst to make high octane gasoline blend stock.
“Isomerization” means a refinery process for rearranging the structure of C5/C6 molecules without changing their size or
chemical composition and is used to improve the octane of C5/C6 gasoline blendstocks.
“LPG” means liquid petroleum gases.
“Lubricant” or “lube” means a solvent neutral paraffinic product used in commercial heavy duty engine oils, passenger
car oils and specialty products for industrial applications such as heat transfer, metalworking, rubber and other general process
oil.
“MSAT2” means Control of Hazardous Air Pollutants from Mobile Sources, a rule issued by the U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency to reduce hazardous emissions from motor vehicles and motor vehicle fuels.
“MEK” means a lube process that separates waxy oil from non-waxy oils using methyl ethyl ketone as a solvent.
“MMBTU” means one million British thermal units.