Sallie Mae 2008 Annual Report Download - page 180
Download and view the complete annual report
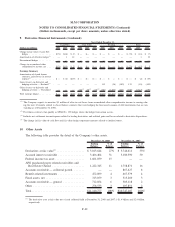
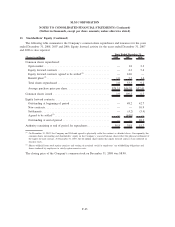
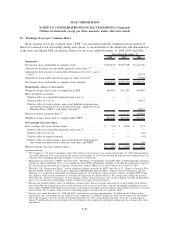
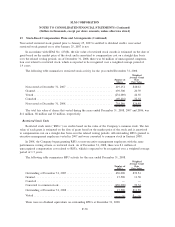
Please find page 180 of the 2008 Sallie Mae annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.9. Derivative Financial Instruments (Continued)
an asset or liability measured at its fair value. As more fully described below, if certain criteria are met,
derivative instruments are classified and accounted for by the Company as either fair value or cash flow
hedges. If these criteria are not met, the derivative financial instruments are accounted for as trading.
Fair Value Hedges
Fair value hedges are generally used by the Company to hedge the exposure to changes in fair value of a
recognized fixed rate asset or liability. The Company enters into interest rate swaps to convert fixed rate assets
into variable rate assets and fixed rate debt into variable rate debt. The Company also enters into cross-
currency interest rate swaps to convert foreign currency denominated fixed and floating debt to U.S. dollar
denominated variable debt. For fair value hedges, the Company generally considers all components of the
derivative’s gain and/or loss when assessing hedge effectiveness (in some cases the Company excludes time-
value components) and generally hedges changes in fair value due to interest rates or interest rates and foreign
currency exchange rates or the total change in fair value.
Cash Flow Hedges
Cash flow hedges are used by the Company to hedge the exposure to variability in cash flows for a
forecasted debt issuance and for exposure to variability in cash flows of floating rate debt. This strategy is
used primarily to minimize the exposure to volatility from future changes in interest rates. Gains and losses on
the effective portion of a qualifying hedge are accumulated in other comprehensive income and ineffectiveness
is recorded immediately to earnings. In the case of a forecasted debt issuance, gains and losses are reclassified
to earnings over the period which the stated hedged transaction impacts earnings. If the stated transaction is
deemed probable not to occur, gains and losses are reclassified immediately to earnings. In assessing hedge
effectiveness, generally all components of each derivative’s gains or losses are included in the assessment. The
Company generally hedges exposure to changes in cash flows due to changes in interest rates or total changes
in cash flow.
Trading Activities
When instruments do not qualify as hedges under SFAS No. 133, they are accounted for as trading where
all changes in fair value of the derivatives are recorded through earnings. The Company sells interest rate
floors (Floor Income Contracts) to hedge the Embedded Floor Income options in student loan assets. The
Floor Income Contracts are written options which under SFAS No. 133 have a more stringent effectiveness
hurdle to meet. Therefore, these relationships do not satisfy hedging qualifications under SFAS No. 133, but
are considered economic hedges for risk management purposes. The Company uses this strategy to minimize
its exposure to changes in interest rates.
The Company also uses basis swaps to minimize earnings variability caused by having different reset
characteristics on the Company’s interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities. These swaps possess a
term of up to 14 years with a pay rate indexed to 91-day Treasury bill, 3-month commercial paper, 52-week
Treasury bill, LIBOR, Prime, or 1-year constant maturity Treasury rates. The specific terms and notional
amounts of the swaps are determined based on management’s review of its asset/liability structure, its
assessment of future interest rate relationships, and on other factors such as short-term strategic initiatives.
SFAS No. 133 requires that when using basis swaps, the change in the cash flows of the hedge effectively
offset both the change in the cash flows of the asset and the change in the cash flows of the liability. The
Company’s basis swaps hedge variable interest rate risk; however, they generally do not meet this effectiveness
test because the index of the swap does not exactly match the index of the hedged assets as required by
SFAS No. 133. Additionally, some of the Company’s FFELP student loans can earn at either a variable or a
F-60
SLM CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
(Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts, unless otherwise stated)