Intel 2001 Annual Report Download - page 47
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 47 of the 2001 Intel annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
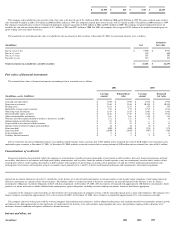
Cash and cash equivalents > Highly liquid debt securities with insignificant interest rate risk and with original maturities of three months or less are classified as cash and cash equivalents.
Investments >
The company's investments consist of:
Trading assets. The company elects to classify as trading assets certain marketable debt and equity securities. The interest, currency and/or equity market risks inherent in these
investments are generally mitigated through the use of derivative instruments. Also included in trading assets is a marketable equity portfolio held to generate returns that offset changes in
liabilities related to certain deferred compensation arrangements. Trading assets are stated at fair value, with gains or losses resulting from changes in fair value recognized currently in
earnings. For marketable debt securities, gains or losses from changes in fair value, offset by losses or gains on related derivatives, are included in interest and other, net. For marketable
equity securities having related derivative instruments, gains or losses from changes in fair value, offset or partially offset by losses or gains on the derivatives, are included in gains (losses)
on equity securities, net. For other marketable equity securities related to deferred compensation arrangements, gains or losses from changes in fair value, offset by losses or gains on the
related liabilities, are included in interest and other, net.
Available-for-sale investments. Investments designated as available-for-sale include marketable debt and equity securities. Investments that are designated as available-for-sale as of the
balance sheet date are reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses, net of tax, recorded in stockholders' equity. The cost of securities sold is based on the specific identification
method. Realized gains and losses on the sale of debt securities are recorded in interest and other, net. Realized gains or losses on the sale or exchange of equity securities and declines in
value judged to be other than temporary are recorded in gains (losses) on equity securities, net. Marketable equity securities are presumed to be impaired if the fair value is less than the cost
basis for six months, absent compelling evidence to the contrary.
Debt securities with original maturities greater than three months and remaining maturities less than one year are classified as short-term investments. Debt securities with remaining
maturities greater than one year are classified as other long-term investments.
The company acquires certain equity investments for the promotion of business and strategic objectives, and to the extent these investments continue to have strategic value, the company
typically does not attempt to reduce or eliminate the inherent market risks. The marketable portion of these investments is classified separately as marketable strategic equity securities.
Non-marketable equity securities and other investments. Non-marketable equity securities and other investments are accounted for at historical cost or, if Intel has significant influence
over the investee, using the equity method. The company's proportionate share of income or losses from investments accounted for under the equity method and any gain or loss on disposal
is recorded in interest and other, net. Non-marketable equity securities and other investments, as well as equity-method investments, are included in other assets. Non-marketable equity
securities are subject to a periodic impairment review, including assessment of the investee's financial condition, the existence of subsequent rounds of financing and the impact of any
relevant contractual preferences, as well as the investee's historical results of operations, projected results and cash flows. Impairment of non-marketable equity investments is recorded in
gains (losses) on equity securities, net.
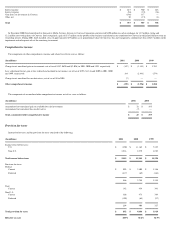
Securities lending >
The company, from time to time, enters into secured lending agreements with financial institutions, generally to facilitate hedging transactions. Selected securities are
loaned for short periods of time and are secured by collateral in the form of cash or securities. The loaned securities continue to be carried as investment assets on the balance sheet. Cash
collateral is recorded as an asset with a corresponding liability. For lending agreements collateralized by securities, the collateral is not recorded as an asset or a liability, unless the collateral
is repledged (see "Short-term debt" under "Borrowings").
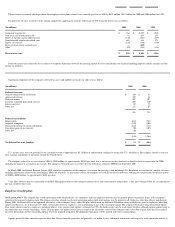
Fair values of financial instruments > Fair values of cash equivalents approximate cost due to the short period of time to maturity. Fair values of short-term investments, trading assets,
marketable strategic equity securities, other long-term investments, certain non-marketable investments, short-term debt, long-term debt, swaps, currency forward contracts, equity options
and warrants are based on quoted market prices or pricing models using current market rates. Debt securities are generally valued using discounted cash flows in an industry-standard yield-
curve model based on LIBOR. Equity options and warrants are priced using a Black-Scholes option valuation model. For certain non-marketable equity securities, fair value is estimated
based on prices recently paid for shares in that company. All of the estimated fair values are management's estimates; however, when there is no readily available market, the fair values may
not necessarily represent the amounts that could be realized in a current transaction.
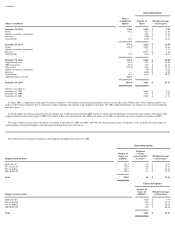
Derivative financial instruments >
The company's primary objective for holding derivative financial instruments is to manage interest rate, non-U.S. currency and some equity market risks.
The company's derivative instruments are recorded at fair value and are included in other current assets, other assets, other accrued liabilities or long-term debt. The company's accounting
policies for these instruments are based on whether they meet the company's criteria for designation as hedging transactions, either as cash flow or fair value hedges. A hedge of the exposure
to variability in the cash flows of an asset or a liability, or of a forecasted transaction, is referred to as a cash flow hedge. A hedge of the exposure to changes in fair value of an asset or a
liability, or of an unrecognized firm commitment, is referred to as a fair value hedge. The criteria for designating a derivative as a hedge include the instrument's effectiveness in risk
reduction and in most cases a one-to-one matching of the derivative instrument to its underlying transaction. Gains and losses on derivatives that are not designated as hedges for accounting
purposes are recognized currently in earnings, and generally offset changes in the values of related assets, liabilities or debt.
As part of its strategic investment program, the company also acquires equity derivative instruments, such as warrants, that are not designated as hedging instruments. The gains or losses
from changes in fair values of these equity derivatives are recognized in gains (losses) on equity securities, net.
Currency risk. The company transacts business in various non-U.S. currencies, primarily Japanese yen and certain other Asian and European currencies. The company has established
revenue, expense and balance sheet risk management programs to protect against reductions in value and volatility of future cash flows caused by changes in exchange rates. The company
uses currency forward contracts, currency options, borrowings in various currencies and currency interest rate swaps in these risk management programs. These programs reduce, but do not
always entirely eliminate, the impact of currency exchange movements.
Currency forward contracts and currency options that are used to hedge exposures to variability in anticipated non-U.S.-dollar- denominated cash flows are designated as cash flow
hedges. The maturities of these instruments are generally less than 12 months. For these derivatives, the effective portion of the gain or loss is reported as a component of other
comprehensive income in stockholders' equity and is reclassified into earnings in the same period or periods in which the hedged transaction affects earnings, and within the same income
statement line item. The ineffective portion of the gain or loss on the derivative in excess of the cumulative change in the present value of future cash flows of the hedged item, if any, is
recognized in interest and other, net during the period of change. Prior to the adoption of SFAS No. 133, derivatives hedging the currency risk of future cash flows were not recognized on the
balance sheet.
Currency interest rate swaps and currency forward contracts are used to offset the currency risk of non-U.S.-dollar-
denominated debt securities classified as trading assets, as well as other
assets and liabilities denominated in various currencies. Changes in fair value of the underlying assets and liabilities are generally offset by the changes in fair value of the related derivatives,
with the resulting net gain or loss, if any, recorded in interest and other, net.
Interest rate risk. The company's primary objective for holding investments in debt securities is to preserve principal while maximizing yields, without significantly increasing risk. To
achieve this objective, the returns on a substantial majority of the company's investments in long-term fixed-rate marketable debt securities are swapped to U.S. dollar LIBOR-based returns,
using interest rate swaps and currency interest rate swaps in transactions that are not designated as hedges for accounting purposes. The floating interest rates on the swaps are reset on a
monthly, quarterly or semiannual basis. Changes in fair value of the debt securities classified as trading assets are generally offset by changes in fair value of the related derivatives, resulting
in negligible net impact. The net gain or loss, if any, is recorded in interest and other, net.