Cathay Pacific 1999 Annual Report Download - page 19
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 19 of the 1999 Cathay Pacific annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Financial Review
23CATHAY PACIFIC AIRWAYS LIMITED ANNUAL REPORT 1999
•Derivative financial instruments which constitute a hedge do not expose the Group to market risk since,
by definition, any change in their market value will be offset by a compensating change in the market value
of the asset, liability or transaction being hedged.
•Exposure to foreign currencies, interest rates and jet fuel price movements are regularly reviewed and
positions are amended in compliance with internal guidelines and limits.
•To manage credit risk, transactions are only carried out with financial institutions of high repute and all
counterparties are subject to prescribed trading limits which are regularly reviewed. Risk exposures are
monitored regularly by reference to market values.
Management of currency and interest rate exposures
•As an international airline, the Group’s revenue streams are denominated in a number of foreign currencies
resulting in exposure to foreign exchange fluctuations.
•To manage this exposure assets are, where possible, financed in those foreign currencies in which net
operating surpluses are anticipated, thus establishing a natural hedge. In addition, the Group uses currency
derivatives to reduce such foreign currency surpluses.
•The use of foreign currency borrowings and currency derivatives to hedge future operating revenues is a key
component of the financial risk management process, as exchange differences realised on the repayment of
financial commitments are effectively matched by the change in value of the foreign currency earnings used
to make those repayments.
•Derivative financial instruments are used to manage the interest rate profile of the foreign currency
commitments.
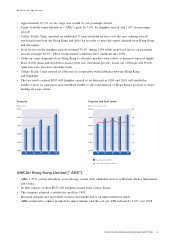
Interest rate profile: borrowings
0
20
40
60
80
100
9998979695
Floating Fixed
%
0
2,000
4,000
6,000
8,000
10,000
OthersUSDJPYHKDGBPEURCHFCADAUD
Within 1 year Between 1-2 years
Between 2-5 years
O thers include KRW, NZ D, SGD and TW D
Over 5 years
Maturity profile by currency: borrowings
HK$ million