Berkshire Hathaway 2008 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
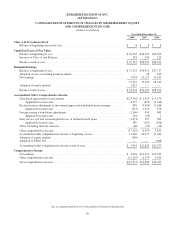
Please find page 37 of the 2008 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices (Continued)
(o) Regulated utilities and energy businesses
Certain domestic energy subsidiaries prepare their financial statements in accordance with SFAS 71, reflecting the
economic effects from the ability to recover certain costs from customers and the requirement to return revenues to
customers in the future through the regulated rate-setting process. Accordingly, certain costs are deferred as regulatory
assets and obligations are accrued as regulatory liabilities which will be amortized over various future periods. At
December 31, 2008, the Consolidated Balance Sheet includes $2,156 million in regulatory assets and $1,506 million
in regulatory liabilities. At December 31, 2007, the Consolidated Balance Sheet includes $1,503 million in regulatory
assets and $1,629 million in regulatory liabilities. Regulatory assets and liabilities are components of other assets and
other liabilities of utilities and energy businesses.
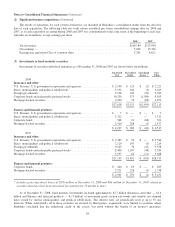
Management continually assesses whether the regulatory assets are probable of future recovery by considering factors
such as applicable regulatory changes, recent rate orders received by other regulated entities and the status of any
pending or potential legislation. If future recovery of costs ceases to be probable, the amount no longer probable of
recovery is charged to earnings.
(p) Foreign currency
The accounts of foreign-based subsidiaries are measured in most instances using the local currency of the subsidiary
as the functional currency. Revenues and expenses of these businesses are generally translated into U.S. Dollars at the
average exchange rate for the period. Assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate as of the end of the
reporting period. Gains or losses from translating the financial statements of foreign-based operations are included in
shareholders’ equity as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income. Gains and losses arising from
transactions denominated in a currency other than the functional currency of Berkshire or the applicable subsidiary of
Berkshire are included in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings except that gains or losses associated with
available-for-sale securities are included as a component of other comprehensive income.
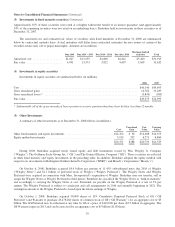
(q) Income taxes
Berkshire and eligible subsidiaries file a consolidated Federal income tax return in the United States. In addition,
Berkshire and subsidiaries also file income tax returns in state, local and foreign jurisdictions as applicable. Provisions
for current income tax liabilities are calculated and accrued on income and expense amounts expected to be included
in the income tax returns for the current year.
Deferred income taxes are calculated under the liability method. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are based
on differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities at the current enacted tax rates.
Changes in deferred income tax assets and liabilities that are associated with components of other comprehensive
income are charged or credited directly to other comprehensive income. Otherwise, changes in deferred income tax
assets and liabilities are included as a component of income tax expense. Changes in deferred income tax assets and
liabilities attributable to changes in enacted tax rates are charged or credited to income tax expense in the period of
enactment. Valuation allowances are established for certain deferred tax assets where realization is not likely.
Assets and liabilities are established for uncertain tax positions taken or positions expected to be taken in income tax
returns when such positions are judged to not meet the “more-likely-than-not” threshold based on the technical merits
of the positions. Estimated interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions are included as a component of
income tax expense.
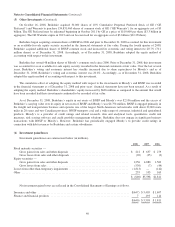
(r) Accounting pronouncements adopted in 2008 and 2007
Effective January 1, 2008, Berkshire adopted the provisions of SFAS 157 with respect to fair value measurements of
financial assets and liabilities. In October 2008, the FASB issued FSP No. 157-3, “Determining the Fair Value of a
Financial Asset When the Market for That Asset Is Not Active” (“FSP FAS 157-3”), which was effective upon issuance.
FSP FAS 157-3 clarifies the application of SFAS 157 in a market that is not active. The effect of adopting SFAS 157 was
not material to Berkshire’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
Effective January 1, 2008, Berkshire adopted the provisions of SFAS No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial
Assets and Financial Liabilities — Including an amendment of FASB Statement No. 115” (“SFAS 159”). SFAS 159
permits entities to elect to measure financial instruments and certain other items at fair value. Upon adoption of SFAS
35