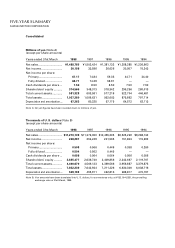
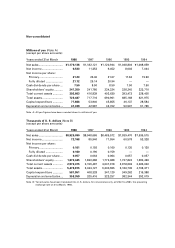
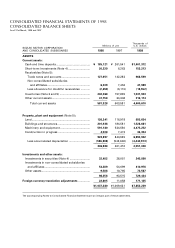
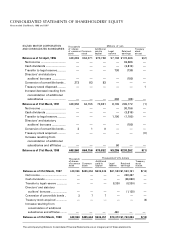
Suzuki 1998 Annual Report Download - page 21
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 21 of the 1998 Suzuki annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1.Basis of presenting consolidated financial statements
The accompanying consolidated financial statements of SUZUKI MOTOR CORPORATION (the
Company) have been prepared on the basis of generally accepted accounting principles
and practices in Japan, and from the consolidated financial statements filed with the
Minister of Finance as required by the Securities and Exchange Law of Japan.
Certain reclassifications and modifications have been made to the original consolidated
financial statements for the convenience of readers outside Japan. In addition,
the consolidated statements of shareholders' equity have been prepared as additional
information, although such statements are not required in Japan, and the notes include
information which is not required under generally accepted accounting principles and
practices in Japan.
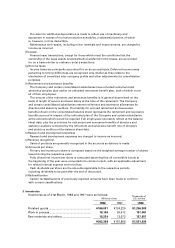
All yen figures have been rounded down to millions of yen. For the convenience of
readers, the consolidated financial statements have been presented in U.S. dollars by
translating all Japanese yen amounts on the basis of ¥132.10 to U.S.$1, the rate of
exchange prevailing as of 31st March, 1998. Consequently, the totals shown in the
consolidated financial statements (both in yen and in U.S.dollars) do not necessarily
agree with the sum of the individual amounts.
2.Summary of significant accounting policies
(a)Principles of consolidation
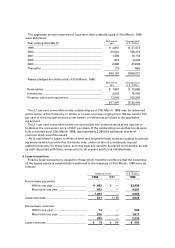
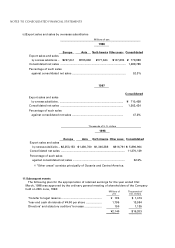
In the consolidated financial statements for the years ended 31st March, 1998 and
1997, the number of consolidated subsidiaries are 134 and 131 respectively. The
Company's remaining subsidiaries, the gross assets, net sales, net income and retained
earnings of which are not significant in the aggregate in relation to the comparable
figures in the consolidated financial statements, have not been consolidated. All
significant inter-company accounts and transactions are eliminated in consolidation.
Investments in certain significant unconsolidated subsidiaries and affiliated
companies (20 per cent to 50 per cent owned) are accounted for by the equity method.
The difference at the time of acquisition between the cost and underlying net equity
of investments in consolidated subsidiaries and in unconsolidated subsidiaries and
affiliated companies accounted for under the equity method is, as a rule, amortized
over a period of five years after appropriate adjustments.
(b)Foreign currency translations
Current receivables and payables in foreign currencies of domestic companies are
translated into Japanese yen at the exchange rates as of the balance sheet date, and
other assets in foreign currencies are translated at the historical rates. Revenue and
costs are translated at exchange rates prevailing during the year. Gains or losses
resulting from translation of foreign currency transactions are credited or charged
to income as incurred.
The balance sheet accounts, revenue and expenses of overseas consolidated subsidiaries
are translated into Japanese yen on the basis of the year-end rates except shareholders'
equity, which are translated at the historical rates.
Translation differences are shown as "Foreign currency translation adjustments" in the
consolidated balance sheets.
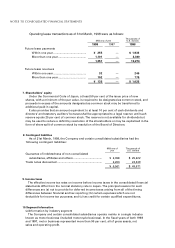
(c)Investments in securities
Marketable securities (current and non-current) are stated at the lower of cost or
market value, cost being determined by the moving average method. Non-marketable
securities are stated at cost determined by the moving average method.
(d)Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market value, cost being determined
principally by the gross average method.
(e)Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is principally computed
by the declining-balance method based on estimated useful lives of the assets.