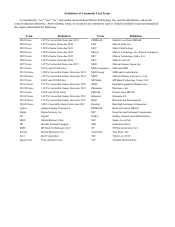
Crucial 2015 Annual Report Download - page 9
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 9 of the 2015 Crucial annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.7
Competition
We face intense competition in the semiconductor memory market from a number of companies, including Intel; Samsung
Electronics Co., Ltd.; SanDisk Corporation; SK Hynix Inc.; and Toshiba Corporation. Some of our competitors are large
corporations or conglomerates that may have greater resources to withstand downturns in the semiconductor markets in which
we compete, invest in technology, and capitalize on growth opportunities. Our competitors seek to increase silicon capacity,
improve yields, reduce die size, and minimize mask levels in their product designs resulting in significantly increased
worldwide supply and downward pressure on prices. Many of our high-volume memory products are manufactured to industry
standard specifications and as such have similar performance characteristics to those of our competitors. For these high-
volume memory products, the principal competitive factors are generally price and performance characteristics including:
operating speed, power consumption, reliability, compatibility, size, and form factors. For our other memory products, the
aforementioned performance characteristics generally take precedence over pricing.
Research and Development
Our process technology R&D efforts are focused primarily on development of successively smaller line-width process
technologies, as well as new, fundamentally different memory structures, materials, and packages, which are designed to
facilitate our transition to next generation memory products. Additional process technology R&D efforts focus on the
enablement of advanced computing and mobile memory architectures, the investigation of new opportunities that leverage our
core semiconductor expertise, and the development of new manufacturing materials. Product design and development efforts
include our high density DDR3 and DDR4 DRAM and LPDRAM products as well as high density and mobile NAND Flash
memory (including 3D NAND and MLC and TLC technologies), 3D XPoint memory, NOR Flash memory, specialty memory,
SSDs, HMCs, and other memory technologies and systems.
Our R&D expenses were $1.54 billion, $1.37 billion, and $931 million in 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. We
generally share with Intel the costs of product design and process development activities for NAND Flash memory and 3D
XPoint memory. Our R&D expenses reflect net reductions of $231 million, $162 million, and $176 million in 2015, 2014, and
2013, respectively, as a result of reimbursements under our Intel and other cost-sharing arrangements.
To compete in the semiconductor memory industry, we must continue to develop technologically advanced products and
processes. We believe that expansion of our semiconductor product offerings is necessary to meet expected market demand for
specific memory solutions. Our process, design, and package development efforts occur at multiple locations across the world,
with our largest R&D center located in Boise, Idaho, and other significant R&D centers in Japan, China, and other sites in the
U.S. In addition, we develop photolithography mask technology at our MP Mask joint venture facility in Boise.
R&D expenses vary primarily with the number of development wafers processed, the cost of advanced equipment
dedicated to new product and process development, and personnel costs. Because of the lead times necessary to manufacture
our products, we typically begin to process wafers before completion of performance and reliability testing. We deem
development of a product complete once the product has been thoroughly reviewed and tested for performance and reliability.
R&D expenses can vary significantly depending on the timing of product qualification.
Geographic Information
Sales to customers outside the United States totaled $13.63 billion for 2015 and included sales of $6.66 billion in China,
$2.24 billion in Taiwan, $1.25 billion in Europe, $1.03 billion in Japan, and $2.04 billion in the rest of the Asia Pacific region
(excluding China, Japan, and Taiwan). Sales to customers outside the United States totaled $13.81 billion for 2014 and $7.56
billion for 2013. As of September 3, 2015, we had net property, plant, and equipment of $3.64 billion in the United States,
$3.24 billion in Singapore, $2.17 billion in Japan, $1.07 billion in Taiwan, $331 million in China, and $96 million in other
countries. (See "Part II – Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data – Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
– Geographic Information" and "Item 1A. Risk Factors.")