Access America 2004 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2004 Access America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to the consolidated financial statements
26
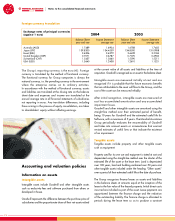
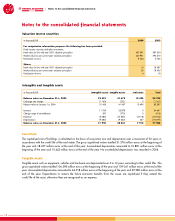
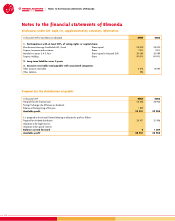
Information on liabilities
Technical provisions
Technical provisions include unearned premium reserves,
claim reserves and other technical provisions.
Premiums written attributable to income of future periods are
accrued under unearned premium reserves. These premiums
are distributed to the current fiscal year and subsequent years
over the period of the contract for every day that the premium
has to cover.
Claim reserves are assessed according to local supervisory
instances’ requirements, are computed on a case by case
basis and are supplemented by IBNR reserves (reserves for
claims Incurred But Not yet Reported) based on management
and statistical estimates.
Non-technical provisions
These include personnel provisions and similar liabilities,
provision for income taxes and other non-technical provisions.
Pension and similar reserves are calculated taking local
circumstances into account as well as expected future trends in
salaries and wages, retirement rates and pension increases.
Defined benefit plans are recognised under IAS 19, using
the method of accruing actuarial gains and losses.
Provision for income taxes are calculated in accordance with
the relevant local tax regulations.
Other liabilities
Other liabilities include deposits received from reinsurers,
loans, liabilities direct /indirect business, liabilities with
associated companies (current accounts), deferred income,
deferred service income and other liabilities. These are reported
at fair value.
Deferred tax liabilities
The calculation of deferred tax is based on temporary
differences between the carrying amounts of assets or liabilities
in the published balance sheet and their tax basis, and on
differences arising from the application of uniform valuation
policies for consolidation purposes. The tax rates used for the
calculation of deferred taxes are the local rates applicable in
the countries concerned. Anticipated changes are already
taken into account as at balance sheet date.
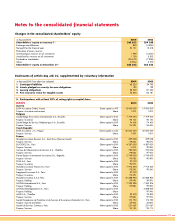
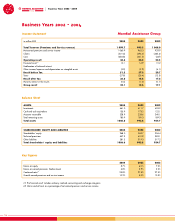
Information on income statement
Turnover
Turnover includes insurance premiums and service revenue.
Premiums earned
Premiums written for travel insurance are reported proportio-
nately as income over the term of the insurance contract for
every day that the premium has to cover. Unearned premiums
are calculated separately for each policy in order to determine
the portion of premium income that has not been earned.
Claims and service administration expenses
(ICHC / ISHC)
Claims and service handling costs are assessed according to
business management criteria and transferred from the general
expenses to the claims and service administration expenses,
respectively.
Ordinary result
Interest income and interest expenses are recognised on an
accrual basis. Dividends are recognised as income when
received. Interest on finance leases is recognised as interest
expenses over the term of the respective lease.
Income Taxes
Income tax expense includes current income taxes and deferred
income taxes. Certain items of income and expense are not
reported in tax returns and financial statements in the same
year. The tax effect of these timing differences is booked as
deferred taxes.
Explanation of the accounting and
valuation policies differing from Swiss law
The most important differences are summarised below.
Shareholders’ equity
Shareholders’ equity increases overall because investments
available for sale are shown in the balance sheet at market
value with the unrealised gains / losses being included under
other reserves.
Claim equalisation reserves
Claim equalisation reserves and major risk reserves are not
allowed under Mondial Assistance Group accounting policy
because they do not represent a present obligation toward
third parties.
Claims reserves
Claims reserves tend to be somewhat lower under Mondial
Assistance Group accounting policy because they are not
calculated in accordance with the prudence concept but at the
best estimate of the ultimate cost.
Acquisition costs
Under Mondial Assistance Group accounting policy acquisition
costs are capitalised and amortised over the term of policy.
Goodwill
Goodwill is amortised through income over its estimated
useful life under Mondial Assistance Group accounting policy,
but not exceeding 10 years.