Holiday Inn 2004 Annual Report Download - page 13
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 13 of the 2004 Holiday Inn annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SHARE PRICE AND MARKET CAPITALISATION
The share price in 2004 fluctuated between 479.17p and 690.81p
and closed at 647.50p on 31 December 2004. This compares
with the share price immediately following the Separation in April
2003 of 372.55p.
At 31 December 2004, the market capitalisation of IHG was
£4.03bn.
TREASURY MANAGEMENT
Treasury policy is to manage financial risks that arise in relation to
underlying business needs. The activities of the treasury function
are carried out in accordance with Board approved policies and
are subject to regular internal audit.
The treasury function does not operate as a profit centre. Treasury
activities include money market investments, spot and forward
foreign exchange instruments, currency options, currency swaps,
interest rate swaps and options, and forward rate agreements.
One of the primary objectives of the Group’s treasury risk
management policy is to protect the financial covenant ratios in
the loan documentation against the adverse impact of movements
in interest rates and foreign exchange rates.
Movements in foreign exchange rates, particularly the US dollar
and euro, can affect the Group’s reported profit, net assets and
interest cover. To hedge this translation exposure as far as
is reasonably practical, borrowings are taken out in foreign
currencies (either directly or via currency swaps), which broadly
match those in which the Group’s major net assets are
denominated.
Interest rate exposure is managed within parameters that stipulate
that fixed rate borrowings should normally account for no less
than 25%, and no more than 75%, of net borrowings for each
major currency. This is achieved through the use of interest rate
swaps and options and forward rate agreements.
Based on the year end net debt position (figure 8), and given the
underlying maturity profile of investments, borrowings and hedging
instruments at that date, a one percentage point rise in US dollar
interest rates would increase the net interest charge by
approximately £2m, whilst a one percentage point rise in euro
interest rates would increase the net interest charge by £6m.
Foreign exchange transaction exposure is managed by the forward
purchase or sale of foreign currencies or the use of currency
options. Most significant exposures of the Group are in currencies
that are freely convertible.
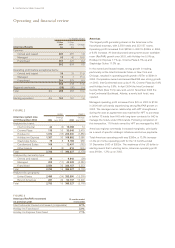
FIGURE 7
31 Dec 31 Dec
Interest risk profile of gross debt 2004 2003
for major currencies %%
At fixed rates 27 59
At variable rates 73 41
FIGURE 8
31 Dec 31 Dec
2004 2003
Net debt £m £m
Borrowings:
Sterling 247 24
US Dollar 335 952
Euro 799 772
Australian Dollar 86 77
Hong Kong Dollar 69 84
Other 226
Cash and current asset investments (422) (1,366)
Total 1,116 569
Note: all shown after the effect of currency swaps.
FIGURE 9
31 Dec 31 Dec
2004 2003
Facilities £m £m
Committed 1,697 962
Uncommitted 64 80
Total 1,761 1,042
InterContinental Hotels Group 2004 11