Blackberry 1998 Annual Report Download - page 18
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 18 of the 1998 Blackberry annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.16
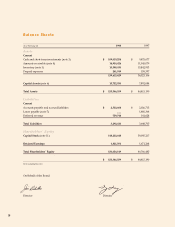
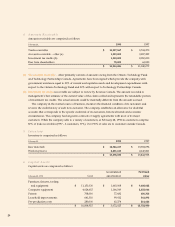
As a result of substantial cash inflows from
financing activities, RIM ended 1998 with a strong
balance sheet. Cash and short-term investments of
$109 million represented more than two-thirds of
total assets, and RIM was virtually debt-free.
Management believes the Company’s current cash
position and existing working capital are sufficient to
meet its foreseeable requirements.
Year 2000 compliance
The Company believes Year 2000 issues will have
a negligible impact on its ongoing operations.
Nonetheless, enterprise-wide programs have been
implemented to identify, test, and minimize RIM’s
exposure to Year 2000 issues. These programs are
examining internal systems and equipment as well
as the risks in the event trading partners, such as
suppliers and customers, are not compliant. An
external consulting firm that specializes in this field is
assisting the Company with these tasks. RIM will take
such steps as deemed necessary to correct any risks or
weaknesses identified by this examination, and
foresees no barriers to taking remedial action. The
costs of Year 2000 programs are not anticipated to
be material and will be expensed as incurred or
capitalized as appropriate as part of the Company’s
normal operating and capital budgets.
Outlook
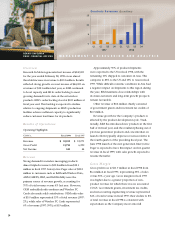
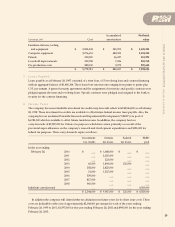
RIM’s order backlog was roughly $100 million at fiscal
year end, most of which is scheduled for delivery in
fiscal 1999. Approximately $90 million of these orders
are for RIM’s next-generation paging products. Sales
of RIM’s OEM radio modem are expected to continue
to contribute to revenue growth, as evidenced by
approximately $6 million in orders received in early
fiscal 1999 from Panasonic Corporation and Mobile
Integrated Technologies. Sales of Wireless PC Cards
should also remain steady during fiscal 1999.
Management’s long-term target is to achieve gross
margin of 35-40%. In fiscal 1999, economies of scale
associated with rising production should increase
RIM’s gross margin above 35%. The 36% gross margin
achieved in the fourth quarter of fiscal 1998 suggests
margins are normalizing as expected.
To maintain market leadership, the Company
expects to apply roughly half of its cash resources to
investments in new equipment, sales and marketing
initiatives, general working capital purposes, and
R&D in 1999. RIM also intends to add roughly 200
new employees in the upcoming year, with up to 25
dedicated to sales and marketing.
R&D is an integral component of the Company’s
long-term product development strategy. Future R&D
expenditures will be maintained at 10% to 15% of
sales, and will continue to be augmented by outside
sources. In May of 1998, Technology Partnerships
Canada entered into an agreement with RIM to invest
$5.7 million in RIM’s $19.1 million R&D initiative for
next-generation two-way messaging products. RIM
should also benefit from the R&D efforts of its
numerous technology partners.
Current trends and industry forecasts indicate
growth for wireless messaging products will escalate.
RIM expects to gain an increasing share of this
expanding market.