3Ware 1999 Annual Report Download - page 12
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 12 of the 1999 3Ware annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
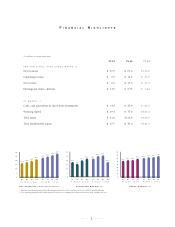
10 1999
AMCC
ATE (AUTOMATED TEST EQUIPMENT) Equipment
that is used for the comprehensive testing of ICs,
printed circuit boards and electronic systems.
Generally, ATE equipment requires ICs that operate
at faster speeds and have more precise timing than the
ICs being tested.
ATM (ASYNCHRONOUS TRANSFER MODE) Ver y
high-speed transmission technology. ATM is a high-
bandwidth, low-delay, connection-oriented, packet-like
switching and multiplexing technique.
BICMOS A process that combines the speed of
bipolar technology with the low power capability
of CMOS technology.
BIPOLAR A process technology that employs silicon
as the substrate upon which to fabricate circuits. The
circuits are based on fast-switching bipolar transistor
structures.
CMOS (COMPLEMENTARY METAL OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR)
A process technology that employs silicon as the sub-
strate upon which to fabricate circuits. The CMOS
integrated circuit design is based on MOS Field Effect
Transistor (FET) structures. CMOS technology offers low
power consumption and small component dimensions.
DATA COMMUNICATIONS The transfer of encoded
information over electrical or optical transmission
systems between points.
DWDM (DENSE WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXING)
A high-speed means of increasing the capacity of
SONET fiber-optic transmission systems through the
multiplexing of multiple wavelengths of light.
FIBRE CHANNEL A set of standards developed by
ANSI (American National Standards Institute). Fibre
Channel provides a practical and inexpensive means
of rapidly transferring data between workstations,
mainframes, supercomputers, desktop computers,
storage devices, displays and other peripherals.
FRAMER A device that adjusts the timing of the
receiver component to coincide with that of the
receiving framing signals.
GIGABIT ETHERNET A local area network standard
used for connecting computers, printers, work-
stations, terminals, servers, etc. within the same
building or campus. Gigabit Ethernet operates over
coaxial and fiber optic cable at speeds of 1.25 Gbps.
Gbps Gigabits per second.
G
LOSSARY
HDTV (HIGH-DEFINITION TELEVISION)Television
offering approximately twice the vertical and horizon-
tal resolution of current NTSC analog television
broadcasting, as well as superior sound quality,
extremely flat screen depth, high reliability and low
power consumption.
MAPPER A device that assigns a logical association of
one set of values, such as addresses on one network,
with quantities or values of another set, such as
devices on another network.
MIXED-SIGNAL IC Monolithic ICs that contain both
digital and analog circuitry.
OC-3,-12,-48,-192 (OPTICAL CARRIER LEVEL-3,
-12,-48,-192) A SONET optical signal. SONET data
rates of 155 Mbps, 622 Mbps, 2.5 Gbps and
9.6 Gbps, respectively.
PMD (PHYSICAL MEDIA DEPENDENT)The sublayer
defining the parameters at the lowest level, such as
speed of the bits on the media.
SDH (SYNCHRONOUS DIGITAL HIERARCHY) A set
of standard fiber optic–based serial standards very
similar to SONET used throughout the world except
in North America and Japan.
SERIAL BACKPLANE A board that distributes signals
serially to various ports of a switching system.
SILICON Traditional semiconducting material used
for fabricating ICs.
SiGe(SILICON GERMANIUM) A process technology
that employs a Germanium-doped silicon substrate
upon which to fabricate circuits. This enables much
higher data rates than are possible with traditional
silicon processes.
SONET (SYNCHRONOUS OPTICAL NETWORK)
SONET is an optical interface standard used
in North America and Japan that allows
interoperability of transmission products from
multiple vendors very similar to SDH. The stan-
dard specifies a family of fiber-optic transmission
rates from 52 Mbps to 10 Gbps, created to provide
the flexibility needed to transport many digital
signals with different capacities and to provide
a design standard for manufacturers.
TELECOMMUNICATIONS The transmission, recep-
tion and the switching of signals, such as electrical or
optical, by wire, fiber or electromagnetic means.